The boxplot() method in Pandas is used to create box plots, which are a standard way of showing the distribution of data through their quartiles.
A box plot displays the distribution of data based on a five-number summary: minimum, first quartile (Q1), median, third quartile (Q3), and maximum.
We use matplotlib.pyplot() to plot the box plot.
Example
import pandas as pd
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
# create a dataframe
data = {'Math': [88, 74, 96, 85, 91],
'Science': [92, 80, 75, 88, 90],
'English': [79, 84, 87, 90, 93]}
df = pd.DataFrame(data)
# create a boxplot
boxplot = df.boxplot()
plt.show()
boxplot() Syntax
The syntax of the boxplot() method in Pandas is:
df.boxplot(column=None, by=None, ax=None, fontsize=None, rot=0, grid=True, figsize=None, layout=None, return_type=None,**kwargs)
boxplot() Arguments
The boxplot() method takes the following arguments:
column(optional): specifies columns to plotby(optional): specifies columns to group byax(optional): matplotlib axes object used to place the plot on specific axes or a subplotfontsize(optional): specifies font size for the axis labelsrot(optional): specifies rotation of axis labelsgrid(optional): whether to display grid lines or notfigsize(optional): specifies size of the figure to createlayout(optional): specifies layout of the boxplotsreturn_type(optional): specifies the type of object to return**kwargs(optional): additional keyword arguments
boxplot() Return Value
The boxplot() method in Pandas can return different types of objects based on the return_type parameter. The return_type parameter specifies the type of object that should be returned. The options are:
'axes': This is the default. Whenreturn_type='axes', the method returns a Matplotlibaxesobject or a NumPy array ofaxesobjects if there are multiple subplots.
'dict': Ifreturn_type='dict', it returns a dictionary whose keys are the column names or group names (if by is specified) and whose values are dictionaries of Matplotliblinesrepresenting the various parts of the box plot.
'both': Whenreturn_type='both', it returns a named tuple with two components:axesandlines, whereaxesis as described above andlinesis a dictionary as in the'dict'return type.
None: Ifreturn_type=None, no object is returned. This might be used in situations where you only want to display the plot and do not need to interact with it programmatically afterward.
Example 1: Simple Box Plot
import pandas as pd
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
# create a dataframe
data = {'Math': [88, 74, 96, 85, 91],
'Science': [92, 80, 75, 88, 90],
'English': [79, 84, 87, 90, 93]}
df = pd.DataFrame(data)
# create a boxplot
boxplot = df.boxplot(column=['Math'])
plt.show()
Output
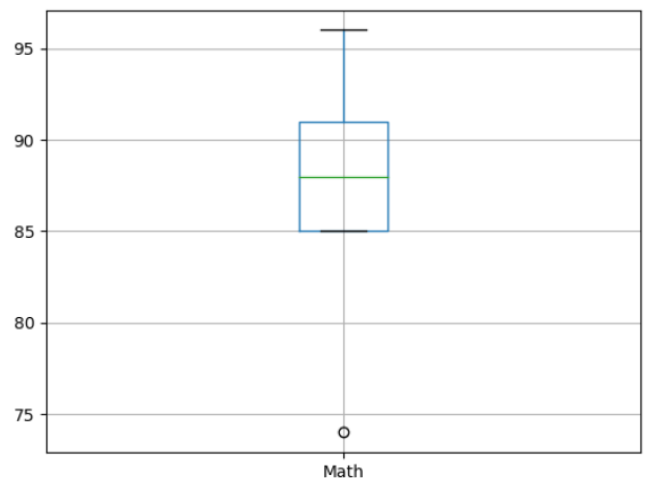
In this example, we plotted a simple box plot for the Math column.
Example 2: Box Plot Grouped by Subject
import pandas as pd
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
# create a dataframe
data = { 'Scores': [88, 74, 96, 91, 92, 80, 88, 90, 79, 87, 90, 93, ],
'Subject': ['Maths', 'Maths', 'Maths', 'Maths', 'Science', 'Science', 'Science', 'Science', 'English', 'English', 'English', 'English']}
df = pd.DataFrame(data)
# create a boxplot grouped by subject
boxplot = df.boxplot(column=['Scores'], by='Subject')
plt.show()
Output
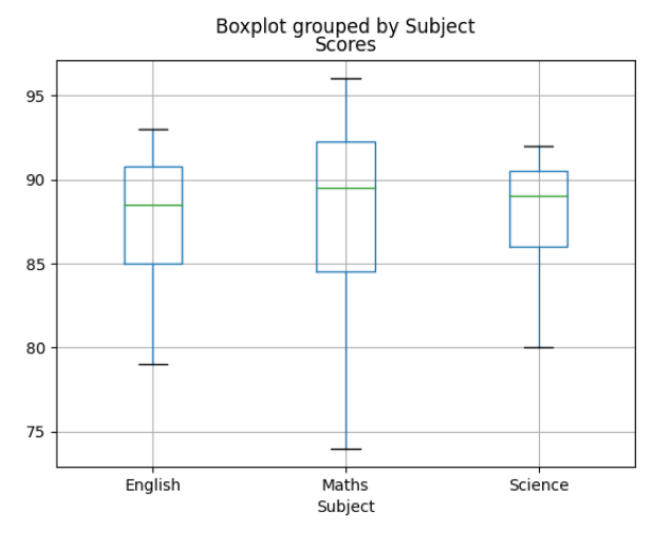
In this example, we used the by argument to group the Scores column by Subject before plotting the box plot.
Example 3: Customizing Box Plots
import pandas as pd
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
# create a dataframe
data = {'Math': [88, 74, 96, 85, 91],
'Science': [92, 80, 75, 88, 90],
'English': [79, 84, 87, 90, 93]}
df = pd.DataFrame(data)
# create a boxplot grouped by subject
boxplot = df.boxplot(column=['Math'], grid=False, rot=45, fontsize=15, figsize=(8,6))
plt.show()
Output
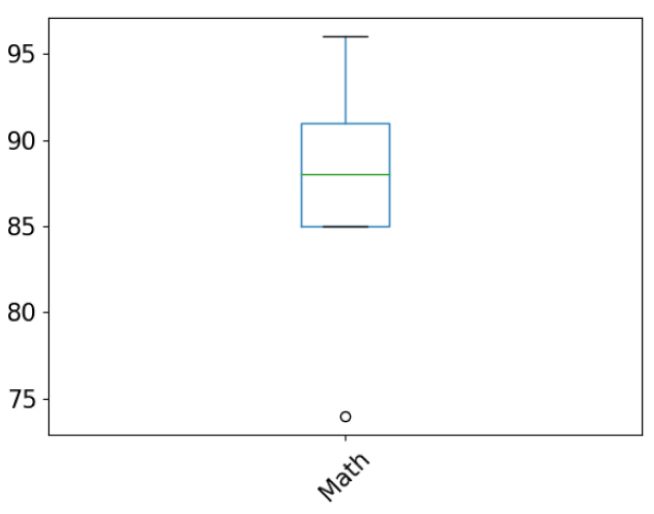
In this example, we customized the box plot for the Math column.
Here,
grid=False: means that the grid lines are not shownrot=45: rotates the label by 45 degreesfontsize=15: sets the font size of labels to 15figsize=(8,6): sets the size of the plot to 8x6 inches
Example4: Pandas boxplot() Return Type
import pandas as pd
# create a dataframe
data = {
'A': [1, 2, 3, 4, 5],
'B': [2, 3, 4, 5, 6],
'C': [3, 4, 5, 6, 7]
}
df = pd.DataFrame(data)
# create a box plot of the data
# with dict return type
plot_dict = df.boxplot(return_type='dict')
print(plot_dict)
Output
{
'whiskers': [<matplotlib.lines.Line2D object at 0x117bf3710>, <matplotlib.lines.Line2D object at 0x117d936d0>, <matplotlib.lines.Line2D object at 0x117da7d10>, <matplotlib.lines.Line2D object at 0x117db4890>, <matplotlib.lines.Line2D object at 0x117dc0a90>, <matplotlib.lines.Line2D object at 0x117dc1610>],
'caps': [<matplotlib.lines.Line2D object at 0x117da4310>, <matplotlib.lines.Line2D object at 0x117da5010>, <matplotlib.lines.Line2D object at 0x117db53d0>, <matplotlib.lines.Line2D object at 0x117db5f50>, <matplotlib.lines.Line2D object at 0x117dc21d0>, <matplotlib.lines.Line2D object at 0x117dc2d90>],
'boxes': [<matplotlib.lines.Line2D object at 0x117d64390>, <matplotlib.lines.Line2D object at 0x117da71d0>, <matplotlib.lines.Line2D object at 0x117db7f10>],
'medians': [<matplotlib.lines.Line2D object at 0x117da5bd0>, <matplotlib.lines.Line2D object at 0x117db6b10>, <matplotlib.lines.Line2D object at 0x117dc3850>],
'fliers': [<matplotlib.lines.Line2D object at 0x117da6250>, <matplotlib.lines.Line2D object at 0x117db7450>, <matplotlib.lines.Line2D object at 0x117dcc310>],
'means': []
}
In this example, we returned the box plot as a Python dictionary. This is useful when we want to interact with the box plot programmatically after creating it.
