An array is a collection of similar types of data. For example,
Suppose we need to record the age of 5 students. Instead of creating 5 separate variables, we can simply create an array.

Creating an array in Go
Here is a syntax to declare an array in Golang.
var array_variable = [size]datatype{elements of array}
Here, the size represents the length of an array. The list of elements of the array goes inside {}.
For example,
// Program to create an array and prints its elements
package main
import "fmt"
func main() {
// declare array variable of type integer
// defined size [size=5]
var arrayOfInteger = [5]int{1, 5, 8, 0, 3}
fmt.Println(arrayOfInteger)
}
Output
[1 5 8 0 3]
In the above example, we have created an array named arrayOfInteger. The int specifies that the array arrayOfIntegers can only store integers.
Other ways to declare a Go array
An array can also be declared without specifying its size. The syntax to declare an array of undefined size is:
var array_variable = [...]datatype{elements of array}
For example,
package main
import "fmt"
func main() {
// declare array variable of type string
// undefined size
var arrayOfString = [...]string{"Hello", "Programiz"}
fmt.Println(arrayOfString)
}
Output
[Hello Programiz]
In the above example, we have created an array named arrayOfString with an undefined size [...].
Note: Here, if [] is left empty, it becomes a slice. So [...] is a must if we want an undefined size array.
Arrays can also be created using the shorthand notation :=. For example,
// Program to create an array using short-hand notation
package main
import "fmt"
func main() {
// declare array variable of type string
// using shorthand notation
arrayOfString := [...]string{"Hello", "Programiz"}
fmt.Println(arrayOfString)
}
Output
[Hello Programiz]
In the above program, we have replaced the traditional syntax of creating an array with a shorthand notation (:=).
Accessing array elements in Golang
In Go, each element in an array is associated with a number. The number is known as an array index.
We can access elements of an array using the index number (0, 1, 2 …). For example,
// Program to access the array elements
package main
import "fmt"
func main() {
languages := [3]string{"Go", "Java", "C++"}
// access element at index 0
fmt.Println(languages[0]) // Go
// access element at index 2
fmt.Println(languages[2]) // C++
}
In the above example, we have created an array named languages.
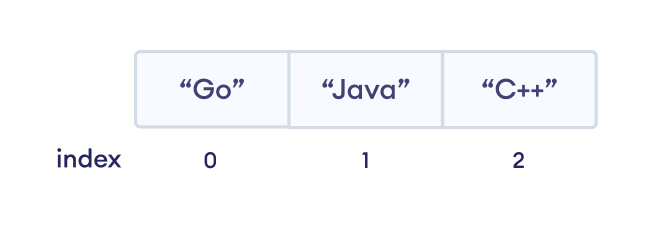
Here, we can see each array element is associated with the index number. And, we have used the index number to access the elements.
Note: The array index always starts with 0. Hence, the first element of an array is present at index 0, not 1.
Initialize an Array in Golang
We can also use index numbers to initialize an array. For example,
package main
import "fmt"
func main() {
// declare an array
var arrayOfIntegers[3] int
// elements are assigned using index
arrayOfIntegers[0] = 5
arrayOfIntegers[1] = 10
arrayOfIntegers[2] = 15
fmt.Println(arrayOfIntegers)
}
Output
[5 10 15]
Here, we have initialized an array arrayOfIntegers using the index number. The arrayOfIntegers[0] = 5 represents that index 0 of arrayOfIntegers holds the value 5, index 1 holds value 10 and so on.
Initialize specific elements of an array
In Golang, we can also initialize the specific element of the array during the declaration. For example,
package main
import "fmt"
func main() {
// initialize the elements of index 0 and 3 only
arrayOfIntegers := [5]int{0: 7, 3: 9}
fmt.Println(arrayOfIntegers)
}
Output
[7 0 0 9 0]
Here, we have initialized the element at index 0 and 3 with values 7 and 9 respectively.
In this case, all other indexes are automatically initialized with value 0 (default value of integer).
Changing the array element in Go
To change an array element, we can simply reassign a new value to the specific index. For example,
// Program to change element by assigning the desired index with a new value
package main
import "fmt"
func main() {
weather := [3]string{"Rainy", "Sunny", "Cloudy"}
// change the element of index 2
weather[2] = "Stromy"
fmt.Println(weather)
}
Output
[Rainy Sunny Stromy]
Here, we have reassigned a new value to index 2 to change the array element from "Cloudy" to "Stromy".
Find the length of an Array in Go
In Golang, we can use the len() function to find the number of elements present inside the array. For example,
package main
import "fmt"
func main() {
// create an array
var arrayOfIntegers = [...]int{1, 5, 8, 0, 3, 10}
// find the length of array using len()
length := len(arrayOfIntegers)
fmt.Println("The length of array is", length)
}
Output
The length of array is 6
Here, we have used len() to find the length of an array arrayOfIntegers.
Looping through an array in Go
In Go, we can also loop through each element of the array. For example,
package main
import "fmt"
func main() {
age := [...]int{12, 4, 5}
// loop through the array
for i := 0; i < len(age); i++ {
fmt.Println(age[i])
}
}
Output
12 4 5
Here, len() function returns the size of an array. The size of an array age is 3 here, so the for loop iterates 3 times; until all 3 elements are printed.
Multidimensional array in Golang
Arrays we have mentioned till now are called one-dimensional arrays. However, we can declare multidimensional arrays in Golang.
A multidimensional array is an array of arrays. That is, each element of a multidimensional array is an array itself. For example,
// Program to illustrate multidimensional array
package main
import "fmt"
func main() {
// create a 2 dimensional array
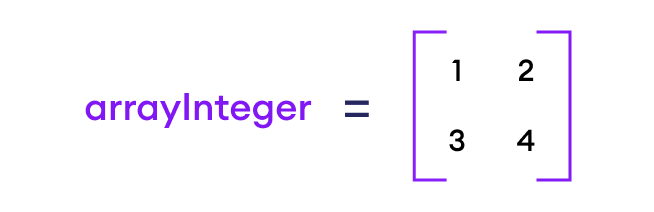
arrayInteger := [2][2]int{{1, 2}, {3, 4}}
// access the values of 2d array
for i := 0; i < 2; i++ {
for j := 0; j < 2; j++ {
fmt.Println(arrayInteger[i][j])
}
}
}
Output
1 2 3 4
Here, we have created a multidimensional array arrayInteger with 2 rows and 2 columns.
A multidimensional array can be treated like a matrix like this