Go break
The break statement terminates the loop when it is encountered. For example,
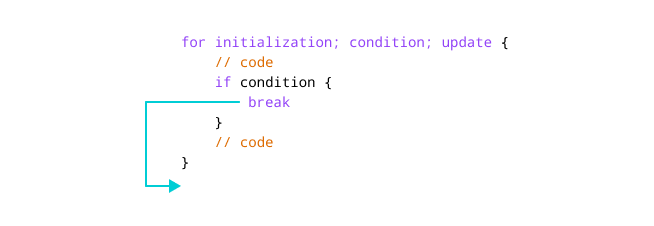
for initialization; condition; update {
break
}
Here, irrespective of the condition of the for loop, the break statement terminates the loop.
Working of Go break statement
Example: Go break statement
package main
import "fmt"
func main() {
for i := 1 ; i <= 5 ; i++ {
// terminates the loop when i is equal to 3
if i == 3 {
break
}
fmt.Println(i)
}
}
Output
1 2
In the above example, we have used the for loop to print the value of i. Notice the use of the break statement,
if i == 3 {
break
}
Here, when i is equal to 3, the break statement terminates the loop. Hence, the output doesn't include values after 2.
Go break statement with nested loops
When we use the break statement with nested loops, it terminates the inner loop. For example,
package main
import "fmt"
func main() {
// outer for loop
for i := 1; i <= 3; i++ {
// inner for loop
for j := 1; j <= 3; j++ {
// terminates the inner for loop only
if i==2 {
break
}
fmt.Println("i=", i, "j=", j)
}
}
}
Output
i = 1, j = 1 i = 1, j = 2 i = 1, j = 3 i = 3, j = 1 i = 3, j = 2 i = 3, j = 3
In the above example, we have used the break statement inside the inner for loop.
if i == 2 {
break
}
Here, when the value of i is 2, the break statement terminates the inner for loop.
Hence, we didn't get any output for value i = 2.
Go continue
In Go, the continue statement skips the current iteration of the loop. It passes the control flow of the program to the next iteration. For example,
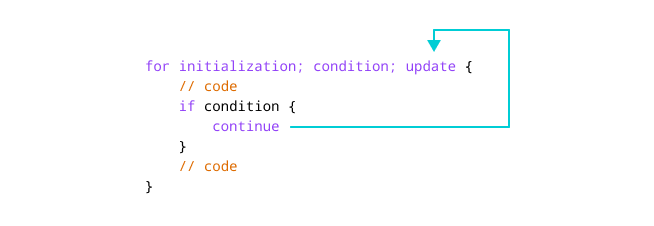
for initialization; condition; update {
if condition {
continue
}
}
Here, irrespective of the condition of the for loop, the continue statement skips the current iteration of the loop.
Working of Go continue statement
Example: Go continue statement
package main
import "fmt"
func main() {
for i := 1 ; i <= 5 ; i++ {
// skips the iteration when i is equal to 3
if i == 3 {
continue
}
fmt.Println(i)
}
}
Output
1 2 4 5
In the above example, we have used the for loop to print the value of i. Notice the use of the continue statement,
if i == 3 {
continue
}
Here, when i is equal to 3, the continue statement is executed. Hence, it skips the current iteration and starts the next iteration. The value 3 is not printed to the output.
Go continue statement with nested loops
When we use the continue statement with nested loops, it skips the current iteration of the inner loop. For example,
package main
import "fmt"
func main() {
for i := 1; i <= 3; i++ {
for j := 1; j <= 3; j++ {
// skips the inner for loop only
if j==2 {
continue
}
fmt.Println("i=", i, "j=",j )
}
}
}
Output
i= 1 j= 1 i= 1 j= 3 i= 2 j= 1 i= 2 j= 3 i= 3 j= 1 i= 3 j= 3
In the above example, we have used the continue statement inside the inner for loop.
if j == 2 {
continue
}
Here, when the value of j is 2, the continue statement is executed. Hence, the value of j = 2 is never displayed in the output.
Note: The break and continue statement is almost always used with decision-making statements. To learn about decision-making, visit Golang if else.