Ruby while Loop
The while loop repeatedly executes a block of code as long as the specified condition is true.
The syntax of the while loop is:
while condition
# Body of loop
end
Here,
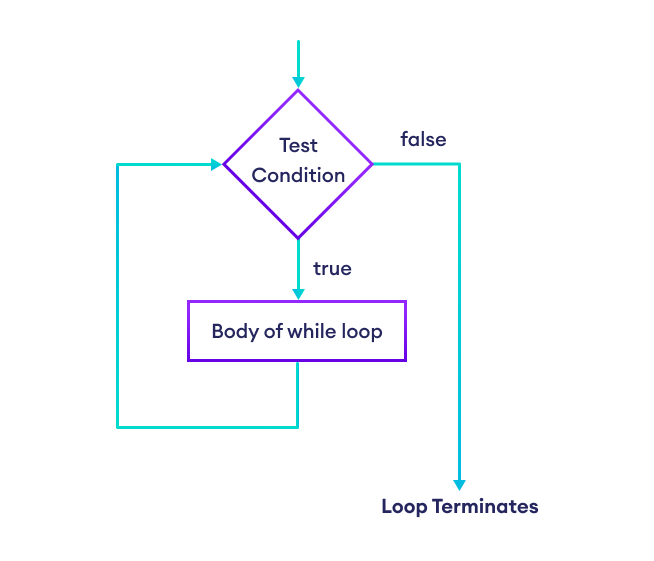
- The
whileloop first evaluates thecondition. - If
conditionevaluates totrue, the loop body is executed. - Then,
conditionis evaluated again. - This process continues as long as
conditionevaluates totrue. - If
conditionevaluates tofalse, the loop stops.
Flowchart of while Loop
Example 1: Display Numbers From 1 to 3
# Initialize variable i
i = 1
# Loop runs until i is less than 4
while i < 4
puts i
# Increase value of i by 1
i += 1
end
Output
1 2 3
Here's how the program works in each iteration of the loop:
| Variable | Condition: i | Action |
|---|---|---|
i = 1 |
true |
1 is printed. i is increased to 2. |
i = 2 |
true |
2 is printed. i is increased to 3. |
i = 3 |
true |
3 is printed. i is increased to 4. |
i = 4 |
false |
The loop is terminated. |
To learn more about loop conditions, visit Ruby Comparison and Logical Operators.
Example 2: Sum of Only Positive Numbers
sum = 0
# Loop as long as input number is positive
while true
print "Enter a number: "
user_input = gets.chomp
# Convert string to integer
input_number = user_input.to_i
# Exit loop if negative
break if input_number < 0
# Add positive number
sum += input_number
end
puts "The sum is #{sum}"
Output
Enter a number: 2 Enter a number: 4 Enter a number: -3 The sum is 6
In the above program,
- We take input from the user using
gets. - We convert the input string to an integer using
.to_i. - If the number is negative, the loop stops using
break. - Otherwise, the number is added to
sum.
Note: In Ruby, inputs are always read as strings. So you must convert them using .to_i for math operations.
Ruby until Loop
The until loop executes a block of code repeatedly until the specified condition becomes true.
It is basically the opposite of the while loop.
The syntax of the until loop is:
until condition
# Body of loop
end
Here,
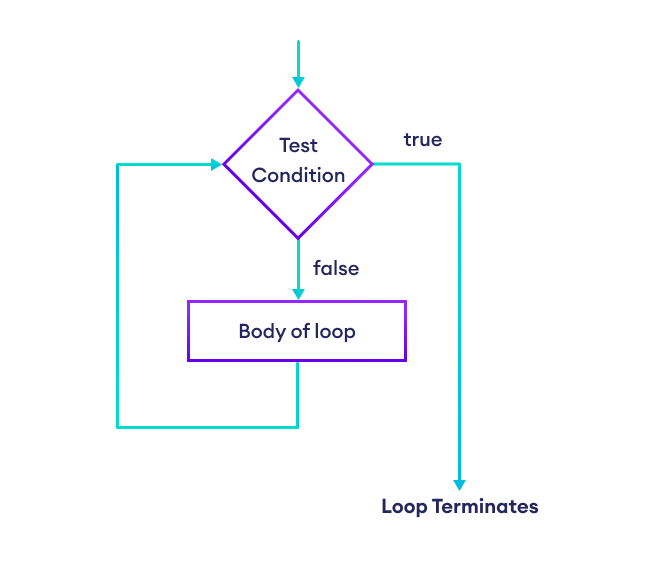
- The
untilloop evaluates thecondition. - If
conditionevaluates tofalse, the code inside the loop runs. - After each iteration,
conditionis checked again. - This process continues as long as
conditionevaluates totrue. - If
conditionevaluates totrue, the loop terminates.
Flowchart of until Loop
Example 3: Display Numbers from 3 to 1
i = 3
# Loop runs until i becomes 0
until i == 0
puts i
# Decrease value of i by 1
i -= 1
end
Output
3 2 1
Here, the initial value of i is 3. Then, we used the until loop to iterate over the values of i. Here's how the loop works in each iteration:
| Action | Variable | Condition: i == 0 |
|---|---|---|
| 3 is printed. i is decreased to 2. | i = 2 |
false |
| 2 is printed. i is decreased to 1. | i = 1 |
false |
| 1 is printed. i is decreased to 0. | i = 0 |
true |
| The loop is terminated. | - | - |
Difference between while and until Loops
The difference between while and until is that they run under opposite conditions.
Ruby while Loop
The while loop runs as long as the condition is true. For example,
i = 5
# False condition
# Body not executed
while i > 10
print "#{i}, "
i += 1
end
# No output
This program will not give any output because the loop runs as long as i is greater than 10. But here, i is 5 and is thus less than 10.
Thus, the loop condition is false and the loop terminates immediately without executing anything.
Ruby until Loop
On the other hand, the until loop executes its body as long as the condition is false. For example,
i = 5
# False condition
# Body is executed
until i > 10
print "#{i}, "
i += 1
end
Output
5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10,
As you can see, the condition i > 10 is false because i is 5, which is less than 10. Thus, the loop prints numbers from 5 to 10.
The moment i becomes 11, the condition i > 10 becomes true and the loop terminates.
Example 4: Sum of Positive Numbers
sum = 0
input_number = 0
# Run the loop at least once
# Keep adding numbers until the user enters a negative value
until input_number < 0
# Add the current number to the sum
sum += input_number
# Ask the user to enter a number
print "Enter a number: "
user_input = gets.chomp
# Convert the input string to an integer
input_number = user_input.to_i
end
# Finally, display the sum
puts "The sum is #{sum}"
Output
Enter a number: 2 Enter a number: 4 Enter a number: -3 The sum is 6
In the above program, the until loop prompts the user to enter a number.
As long as we enter positive numbers, the loop adds them and asks for more input.
If we enter a negative number, the loop terminates without adding the negative number.
More on Ruby while Loop
An infinite while loop is a condition where the loop runs infinitely, as its condition is always true. For example,
i = 1
# Condition is always true
while i < 5
puts i
end
Also, here is an example of an infinite until loop:
i = 1
# Condition never becomes true
until i > 5
puts i
end
In both cases, the condition never stops the loop, so the code runs endlessly.
Note: Infinite loops can cause your program to crash. So, avoid creating them unintentionally.
1. for Loop
We use a for loop when we know the exact number of iterations required. For example,
# Display "hi" 3 times
for i in 1..3
puts "hi"
end
puts "bye"
Output
hi hi hi bye
Here, we know we need to print "hi" three times. So, we've used a for loop instead of a while loop.
2. while Loop
Meanwhile, we use a while loop when the termination condition can vary. For example,
# Boolean variable to use as loop condition
is_display = true
# Variable to store user input
user_choice = nil
# Display "hi" as long as user wants
# Basically, run the loop as long as is_display is true
while is_display
puts "hi"
# Get user input
print "Print hi again? y for yes: "
user_choice = gets.chomp
# Set is_display to false if user_choice is not "y"
is_display = false if user_choice != "y"
end
puts "bye"
Output
hi print hi again? y for yes: y hi print hi again? y for yes: y hi print hi again? y for yes: n bye
In the above program, we let the user print "hi" as much as they desire.
Since we don't know the user's decision, we use a while loop instead of a for loop.