In Python, we use a while loop to repeat a block of code until a certain condition is met. For example,
number = 1
while number <= 3:
print(number)
number = number + 1
Output
1 2 3
In the above example, we have used a while loop to print the numbers from 1 to 3. The loop runs as long as the condition number <= 3 is True.
while Loop Syntax
while condition:
# body of while loop
Here,
- The
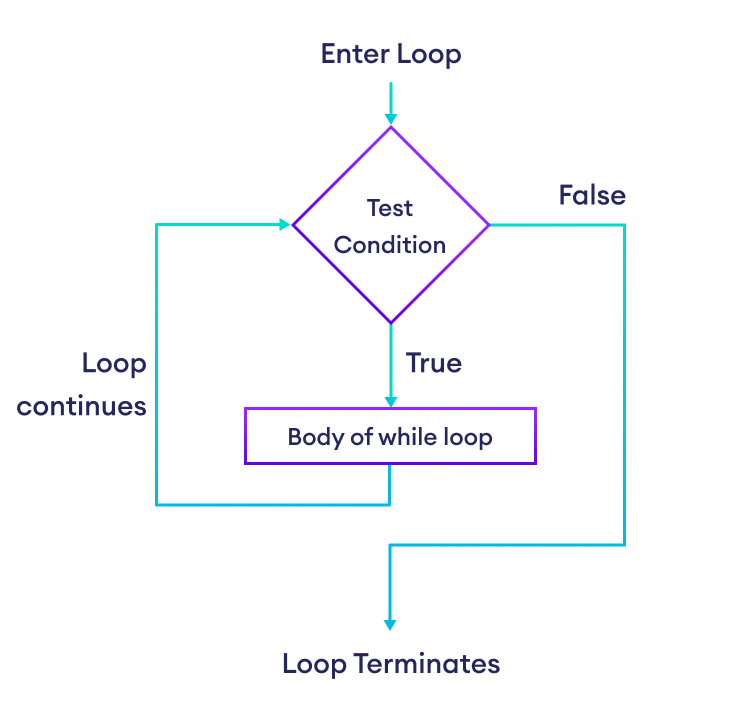
whileloop evaluates condition, which is a boolean expression. - If the condition is
True, body of while loop is executed. The condition is evaluated again. - This process continues until the condition is
False. - Once the condition evaluates to
False, the loop terminates.
Tip: We should update the variables used in condition inside the loop so that it eventually evaluates to False. Otherwise, the loop keeps running, creating an infinite loop.
Flowchart of Python while Loop
Example: Python while Loop
# Print numbers until the user enters 0
number = int(input('Enter a number: '))
# iterate until the user enters 0
while number != 0:
print(f'You entered {number}.')
number = int(input('Enter a number: '))
print('The end.')
Output
Enter a number: 3 You entered 3. Enter a number: 1 You entered 1. Enter a number: -4 You entered -4. Enter a number: 0 The end.
Here is how the above program works:
- It asks the user to enter a number.
- If the user enters a number other than 0, it is printed.
- If the user enters 0, the loop terminates.
Infinite while Loop
If the condition of a while loop always evaluates to True, the loop runs continuously, forming an infinite while loop. For example,
age = 32
# The test condition is always True
while age > 18:
print('You can vote')
Output
You can vote You can vote You can vote . . .
The above program is equivalent to:
age = 32
# the test condition is always True
while True:
print('You can vote')
More on Python while Loop
while loop with break statement
We can use a break statement inside a while loop to terminate the loop immediately without checking the test condition. For example,
while True:
user_input = input('Enter your name: ')
# terminate the loop when user enters end
if user_input == 'end':
print(f'The loop is ended')
break
print(f'Hi {user_input}')
Output
Enter your name: Kevin Hi Kevin Enter your name: end The loop is ended
Here, the condition of the while loop is always True. However, if the user enters end, the loop termiantes because of the break statement.
while loop with an else clause
while loop can have an optional else clause - that is executed once the loop condition is False. For example,
counter = 0
while counter < 2:
print('This is inside loop')
counter = counter + 1
else:
print('This is inside else block')
Output
This is inside loop This is inside loop This is inside else block
Here, on the third iteration, the counter becomes 2 which terminates the loop. It then executes the else block and prints This is inside else block.
Note: The else block will not execute if the while loop is terminated by a break statement.
The for loop is usually used in the sequence when the number of iterations is known. For example,
# loop is iterated 4 times
for i in range(4):
print(i)
Output
0 1 2 3
The while loop is usually used when the number of iterations is unknown. For example,
while True:
user_input = input("Enter password: ")
# terminate the loop when user enters exit
if user_input == 'exit':
print(f'Status: Entry Rejected')
break
print(f'Status: Entry Allowed')
Output
Enter password: Python is Fun Status: Entry Allowed Enter password: exit Status: Entry Rejected
Also Read:
