Arrays are ordered collections that can hold elements of any data type, including numbers, strings, other arrays, or even objects.
Here's a simple example of arrays. You can read the rest of the tutorial to learn more.
Example
ages = [10, 12, 3, 40, 5]
puts ages.inspect
# Output
# [10, 12, 3, 40, 5]
Here, ages is an array of numbers representing different ages.
Creating an Array
In Ruby, you can create an array by enclosing a list of elements in square brackets ([]).
For instance, to store the names of students in a class, you'd write:
student_names = ["Alice", "Bob", "Charlie"]
Note: You can also create an empty array using [] or Array.new. For example,
student_names1 = []
student_names2 = Array.new
Printing an Array
You can print an array in the following ways:
1. Using the .inspect method.
The .inspect method returns a string representation of an object, i.e., how Ruby internally represents the object. For example,
student_names = ["Alice", "Bob", "Charlie"]
puts student_names.inspect
# Output: ["Alice", "Bob", "Charlie"]
As you can see, Ruby internally represents the student_names array as ["Alice", "Bob", "Charlie"].
Note: You can get a similar output using print or p without .inspect. For example,
print student_names
p student_names
However, keep in mind the following:
printwon't add a newline after your output.pisn't ideal for string interpolation.
2. Using puts without .inspect.
You can use puts without .inspect if you want to print each element in a new line. For example,
student_names = ["Alice", "Bob", "Charlie"]
puts student_names
Output
Alice Bob Charlie
Accessing Array Elements
Once an array is created, you can access its elements by their indexes.
The index of an array starts from 0, meaning the first element is at index 0, the second at index 1, and so on. For example,
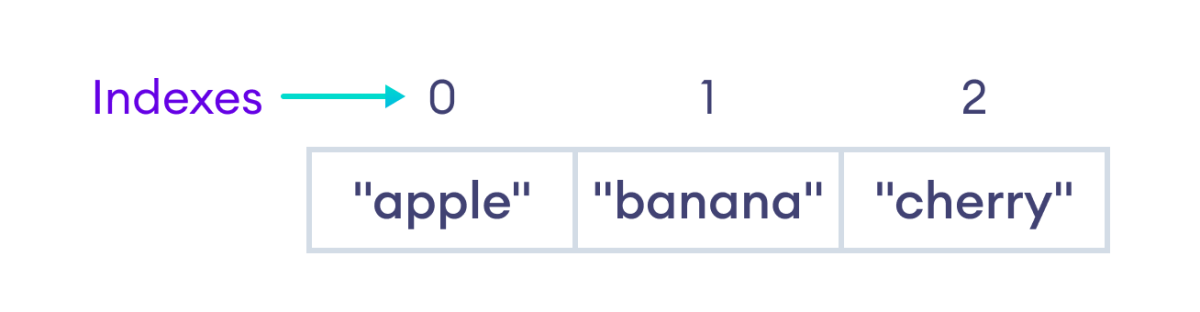
Example
fruits = ["apple", "banana", "cherry"]
first_fruit = fruits[0]
second_fruit = fruits[1]
puts first_fruit
puts second_fruit
Output
apple banana
Operations in an Array
You can perform various operations on an array, such as adding, removing, and changing its elements.
Let's see each of the operations in detail.
Adding Elements to an Array
You can use the push method to add one or more elements to the end of an array. For example,
fruits = ["apple", "banana", "cherry"]
# Add "orange" to the end of the array
fruits.push("orange")
puts fruits.inspect
Output
["apple", "banana", "cherry", "orange"]
You can also use a shovel operator (<<) to add one or more elements to the end of an array. For example,
fruits = ["apple", "banana", "cherry"]
fruits << "mango" << "pineapple"
puts fruits.inspect
Output
["apple", "banana", "cherry", "mango", "pineapple"]
Removing Elements From an Array
You can use the pop method to remove the last element from an array. For example,
fruits = ["apple", "banana", "cherry"]
last = fruits.pop
puts fruits.inspect
puts last
Output
["apple", "banana"] cherry
As you can see, the pop method removes the last element and returns it. We then stored this returned value in the last variable.
Changing Elements in an Array
You can change an element in an array by assigning a new value to the specified index. For example,
fruits = ["apple", "banana", "cherry"]
puts "Before changing, the second element is: #{fruits[1]}"
fruits[1] = "mango"
puts "After changing, the second element is: #{fruits[1]}"
Output
Before changing, the second element is banana After changing, the second element is mango
Array Methods
There are several other array methods you can use to perform various operations. These methods are summarized in the table below:
| Method | Description |
|---|---|
concat |
Joins two or more arrays and returns the result. |
join |
Converts an array to a string with a given separator. |
index |
Returns the index of the first matching element. |
find / detect |
Returns the first element that satisfies a condition. |
each |
Runs a block for each element in the array. |
include? |
Checks if the array contains a specific element. |
sort |
Sorts the array in place (or use sort for a copy). |
slice |
Selects part of an array and returns it as a new array. |
slice! |
Changes the contents of an array by removing elements at a given index and returning them. |
insert |
Adds one or more elements at a specific index of an array. |
Example: Array Methods
Let's look at an example to see how some of the above methods work.
array1 = [1, 2, 3]
array2 = [4, 5, 6]
# Use concat to merge array1 and array2
combined_array = array1.concat(array2)
puts "Combined Array: #{combined_array.inspect}"
# Use index to find the index of element 5 in combined_array
index = combined_array.index(5)
puts "Index of 5: #{index}"
# Use slice to get a portion of combined_array (elements from index 1 to 3)
sliced_array = combined_array.slice(1, 3)
puts "Sliced Array: #{sliced_array.inspect}"
# Use slice! to remove two elements starting from index 3
combined_array.slice!(3, 2)
puts "Array After Removing 4 and 5: #{combined_array.inspect}"
# Use insert to add elements 7, 8 at index 3
combined_array.insert(3, 7, 8)
puts "Array After Inserting 7 and 8: #{combined_array.inspect}"
Output
Combined Array: [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6] Index of 5: 4 Sliced Array: [2, 3, 4] Array After Removing 4 and 5: [1, 2, 3, 6] Array After Inserting 7 and 8: [1, 2, 3, 7, 8, 6]
Frequently Asked Questions
You can also create an array using Array.new. For example,
1. Create an empty array.
empty_array = Array.new
2. Create an array of specified length.
# Creates an array with 5 empty slots
array_with_size = Array.new(5)
3. Create an array of a specific size with a default value
# Array with 4 elements
# Each element has 0 as a value
array_with_elements = Array.new(4,0)
4. Create an array with elements.
arr = Array.new(4) { |i| [1, 2, 3, 4][i] }
Ruby allows negative indexing, which lets you access elements from the end:
- -1 gives the last element.
- -2 the second-last.
- And so on.
Example
fruits = ["apple", "banana", "cherry"]
puts fruits[-1] # Output: cherry
puts fruits[-2] # Output: banana
You can add one or more elements to the beginning of an array using the unshift method. For example,
fruits = ["apple", "banana", "cherry"]
# Add "strawberry" to the beginning of the array
fruits.unshift("strawberry")
puts fruits.inspect
# Output: ["strawberry", "apple", "banana", "cherry"]
You can remove the first element of an array using the shift method. For example,
fruits = ["apple", "banana", "cherry"]
first = fruits.shift
puts fruits.inspect
puts first
Output
["banana", "cherry"] apple