An array is a variable that can store multiple values. For example, if you want to store 100 integers, you can create an array for it.
int data[100];How to declare an array?
dataType arrayName[arraySize];
For example,
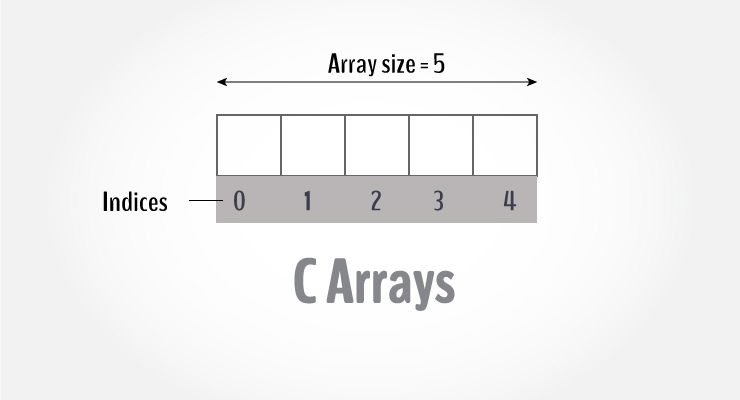
float mark[5];Here, we declared an array, mark, of floating-point type. And its size is 5. Meaning, it can hold 5 floating-point values.
It's important to note that the size and type of an array cannot be changed once it is declared.
Access Array Elements
You can access elements of an array by indices.
Suppose you declared an array mark as above. The first element is mark[0], the second element is mark[1] and so on.
Few keynotes:
- Arrays have 0 as the first index, not 1. In this example, mark[0] is the first element.
- If the size of an array is n, to access the last element, the
n-1index is used. In this example, mark[4] - Suppose the starting address of
mark[0]is 2120d. Then, the address of themark[1]will be 2124d. Similarly, the address ofmark[2]will be 2128d and so on.
This is because the size of afloatis 4 bytes.
How to initialize an array?
It is possible to initialize an array during declaration. For example,
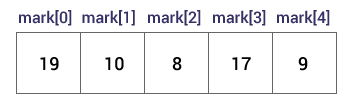
int mark[5] = {19, 10, 8, 17, 9};
You can also initialize an array like this.
int mark[] = {19, 10, 8, 17, 9};
Here, we haven't specified the size. However, the compiler knows its size is 5 as we are initializing it with 5 elements.
Here,
mark[0] is equal to 19 mark[1] is equal to 10 mark[2] is equal to 8 mark[3] is equal to 17 mark[4] is equal to 9
Change Value of Array elements
int mark[5] = {19, 10, 8, 17, 9}
// make the value of the third element to -1
mark[2] = -1;
// make the value of the fifth element to 0
mark[4] = 0;
Input and Output Array Elements
Here's how you can take input from the user and store it in an array element.
// take input and store it in the 3rd element
scanf("%d", &mark[2]);
// take input and store it in the ith element
scanf("%d", &mark[i-1]);
Here's how you can print an individual element of an array.
// print the first element
printf("%d", mark[0]);
// print the third element
printf("%d", mark[2]);
// print the ith element\
printf("%d", mark[i-1]);
Example 1: Array Input/Output
// Program to take 5 values from the user and store them in an array
// Print the elements stored in the array
#include <stdio.h>
int main() {
int values[5];
printf("Enter 5 integers: ");
// taking input and storing it in an array
for(int i = 0; i < 5; ++i) {
scanf("%d", &values[i]);
}
printf("Displaying integers: ");
// printing elements of the array
for(int i = 0; i < 5; ++i) {
printf("%d\n", values[i]);
}
return 0;
}
Output
Enter 5 integers: 1 -3 34 0 3 Displaying integers: 1 -3 34 0 3
Here, we have used a for loop to take five inputs and store them in an array. Then, these elements are printed using another for loop.
Example 2: Calculate Average
// Program to find the average of n numbers using arrays
#include <stdio.h>
int main() {
int marks[10], i, n, sum = 0;
double average;
printf("Enter number of elements: ");
scanf("%d", &n);
for(i=0; i < n; ++i) {
printf("Enter number%d: ",i+1);
scanf("%d", &marks[i]);
// adding integers entered by the user to the sum variable
sum += marks[i];
}
// explicitly convert the sum to double
// then calculate average
average = (double) sum / n;
printf("Average = %.2lf", average);
return 0;
}
Output
Enter number of elements: 5 Enter number1: 45 Enter number2: 35 Enter number3: 38 Enter number4: 31 Enter number5: 49 Average = 39.60
Here, we have computed the average of n numbers entered by the user.
Access elements out of its bound!
Suppose you declared an array of 10 elements. Let's say,
int testArray[10];
You can access the array elements from testArray[0] to testArray[9].
Now let's say if you try to access testArray[12]. The element is not available. This may cause unexpected output (undefined behavior). Sometimes, you might get an error, and some other times your program may run correctly.
Hence, you should never access elements of an array outside of its bound.
Multidimensional arrays
In this tutorial, you learned about arrays. These arrays are called one-dimensional arrays.
In the next tutorial, you will learn about multidimensional arrays (array of an array).
