Example: Java Program to count the number of leaf nodes in a tree
class Node {
int item;
Node left, right;
public Node(int key) {
item = key;
left = right = null;
}
}
class Main {
// root of Tree
Node root;
Main() {
root = null;
}
// method to count leaf nodes
public static int countLeaf(Node node) {
if(node == null) {
return 0;
}
// if left and right of the node is null
// it is leaf node
if (node.left == null && node.right == null) {
return 1;
}
else {
return countLeaf(node.left) + countLeaf(node.right);
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
// create an object of Tree
Main tree = new Main();
// create nodes of tree
tree.root = new Node(5);
tree.root.left = new Node(3);
tree.root.right = new Node(8);
// create child nodes of left child
tree.root.left.left = new Node(2);
tree.root.left.right = new Node(4);
// create child nodes of right child
tree.root.right.left = new Node(7);
tree.root.right.right = new Node(9);
// call method to count leaf nodes
int leafNodes = countLeaf(tree.root);
System.out.println("Total Leaf Nodes = " + leafNodes);
}
}
Output
Total Leaf Nodes = 4
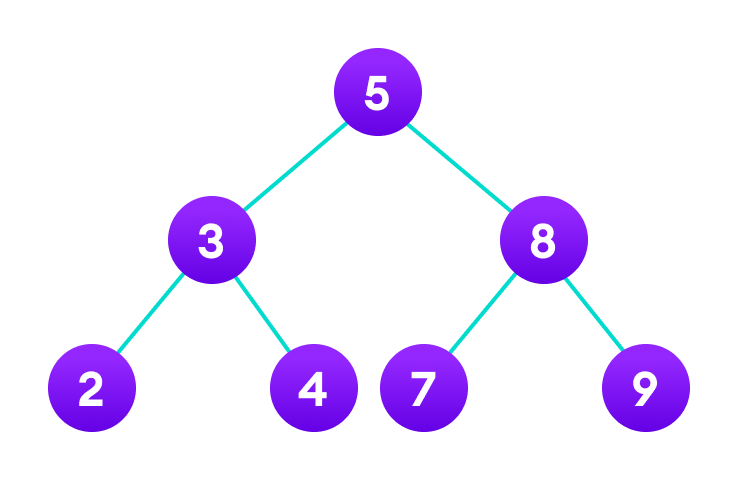
In the above example, we have implemented the tree data structure in Java. Here, we are using recursionto count the number of leaf nodes in the tree.