In C++, an array is a variable that can store multiple values of the same type. For example,
Suppose a class has 27 students, and we need to store all their grades. Instead of creating 27 separate variables, we can simply create an array:
double grade[27];
Here, grade is an array that can hold a maximum of 27 elements of double type.
In C++, the size and type of arrays cannot be changed after its declaration.
C++ Array Declaration
dataType arrayName[arraySize];
For example,
int x[6];
Here,
int- type of element to be stored- x - name of the array
6- size of the array
Access Elements in C++ Array
In C++, each element in an array is associated with a number. The number is known as an array index. We can access elements of an array by using those indices.
// syntax to access array elements
array[index];
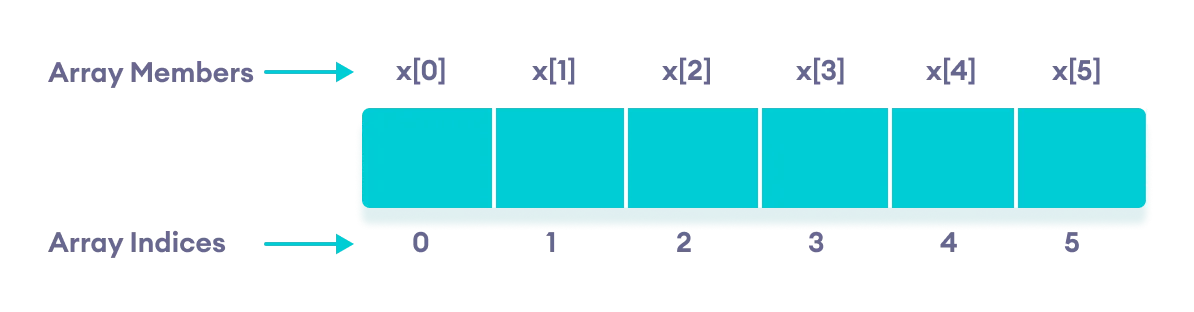
Consider the array x we have seen above.
Few Things to Remember:
- The array indices start with 0. Meaning x[0] is the first element stored at index 0.
- If the size of an array is
n, the last element is stored at index(n-1). In this example, x[5] is the last element. - Elements of an array have consecutive addresses.
For example, suppose the starting address of x[0] is 2120.
Then, the address of the next element x[1] will be 2124, the address of x[2] will be 2128, and so on.
Here, the size of each element is increased by 4. This is because the size of int is 4 bytes.
C++ Array Initialization
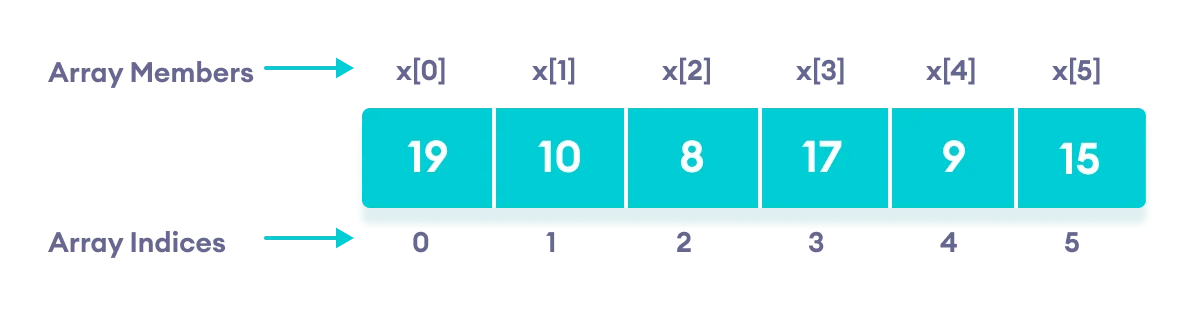
In C++, it's possible to initialize an array during declaration. For example,
// declare and initialize an array
int x[6] = {19, 10, 8, 17, 9, 15};
Another method to initialize array during declaration:
// declare and initialize an array
int x[] = {19, 10, 8, 17, 9, 15};
Here, we have not mentioned the size of the array. In such cases, the compiler automatically computes the size.
C++ Array With Empty Members
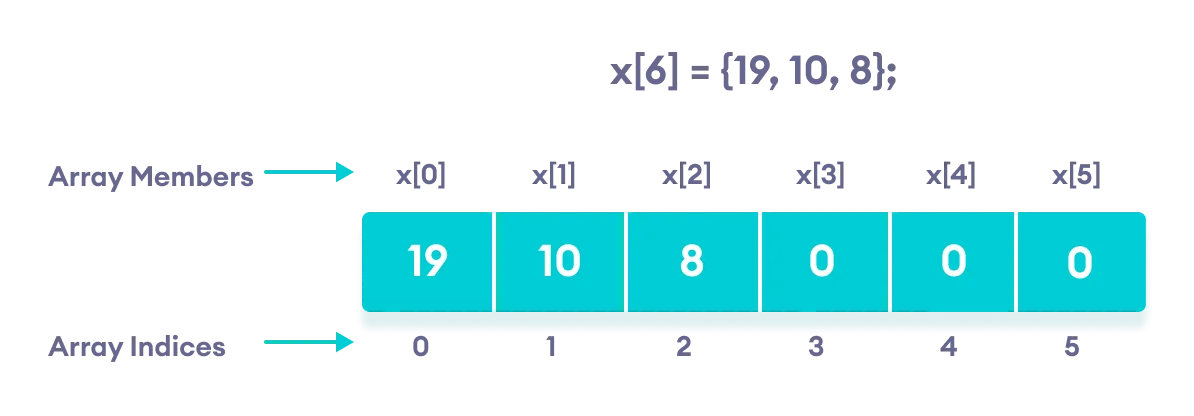
In C++, if an array has a size n, we can store up to n number of elements in the array. However, what will happen if we store less than n number of elements.
For example,
// store only 3 elements in the array
int x[6] = {19, 10, 8};
Here, the array x has a size of 6. However, we have initialized it with only 3 elements.
In such cases, the compiler assigns random values to the remaining places. Often, this random value is simply 0.
How to Insert and Print Array Elements?
int mark[5] = {19, 10, 8, 17, 9}
// change 4th element to 9
mark[3] = 9;
// take input from the user
// store the value at third position
cin >> mark[2];
// take input from the user
// insert at ith position
cin >> mark[i-1];
// print first element of the array
cout << mark[0];
// print ith element of the array
cout >> mark[i-1];
Example 1: Displaying Array Elements
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main() {
int numbers[5] = {7, 5, 6, 12, 35};
cout << "The numbers are: ";
// Printing array elements
// using range based for loop
for (int n : numbers) {
cout << n << " ";
}
cout << "\nThe numbers are: ";
// Printing array elements
// using traditional for loop
for (int i = 0; i < 5; ++i) {
cout << numbers[i] << " ";
}
return 0;
}
Output
The numbers are: 7 5 6 12 35 The numbers are: 7 5 6 12 35
Here, we have used a for loop to iterate from i = 0 to i = 4. In each iteration, we have printed numbers[i].
We again used a range-based for loop to print out the elements of the array. To learn more about this loop, check C++ Ranged for Loop.
Example 2: Take Inputs from User and Store Them in an Array
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main() {
int numbers[5];
cout << "Enter 5 numbers: " << endl;
// store input from user to array
for (int i = 0; i < 5; ++i) {
cin >> numbers[i];
}
cout << "The numbers are: ";
// print array elements
for (int n = 0; n < 5; ++n) {
cout << numbers[n] << " ";
}
return 0;
}
Output
Enter 5 numbers: 11 12 13 14 15 The numbers are: 11 12 13 14 15
Once again, we have used a for loop to iterate from i = 0 to i = 4. In each iteration, we took input from the user and stored it in numbers[i].
Then, we used another for loop to print all the array elements.
C++ Array Out of Bounds
If we declare an array of size 10, then the array will contain elements from index 0 to 9.
However, if we try to access the element at index 10 or more than 10, it will result in an undefined behavior.
This type of error is likely when we use a normal for loop and we access the array element using the [] operator.
Note:To overcome this type of error we should prefer range based for loop where no such operators are needed to access the array elements.
Example 3: Display Sum and Average of Array Elements Using for Loop
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main() {
// initialize an array without specifying size
double numbers[] = {7, 5, 6, 12, 35, 27};
double sum = 0;
double count = 0;
double average;
cout << "The numbers are: ";
// print array elements
// use of range-based for loop
for (const double &n : numbers) {
cout << n << " ";
// calculate the sum
sum += n;
// count the no. of array elements
++count;
}
// print the sum
cout << "\nTheir Sum = " << sum << endl;
// find the average
average = sum / count;
cout << "Their Average = " << average << endl;
return 0;
}
Output
The numbers are: 7 5 6 12 35 27 Their Sum = 92 Their Average = 15.3333
In this program:
- We have initialized a
doublearray named numbers but without specifying its size. We also declared threedoublevariables: sum, count, and average.
Here,sum =0andcount = 0. - Then we used a range-based
forloop to print the array elements. In each iteration of the loop, we add the current array element to sum. - We also increase the value of count by
1in each iteration, so that we can get the size of the array by the end of the for loop. - After printing all the elements, we print the sum and the average of all the numbers. The average of the numbers is given by
average = sum / count;
Also Read