In programming, loops are used to repeat a block of code. For example, if you want to show a message 100 times, then you can use a loop. It's just a simple example, you can achieve much more with loops.
In the previous tutorial, you learned about the Swift for-in Loop. Here, you are going to learn about while and repeat...while loops.
Swift while Loop
Swift while loop is used to run a specific code until a certain condition is met.
The syntax of while loop is:
while (condition){
// body of loop
}
Here,
- A
whileloop evaluatesconditioninside the parenthesis(). - If
conditionevaluates totrue, the code inside thewhileloop is executed. conditionis evaluated again.- This process continues until the
conditionisfalse. - When
conditionevaluates tofalse, the loop stops.
Flowchart of while Loop
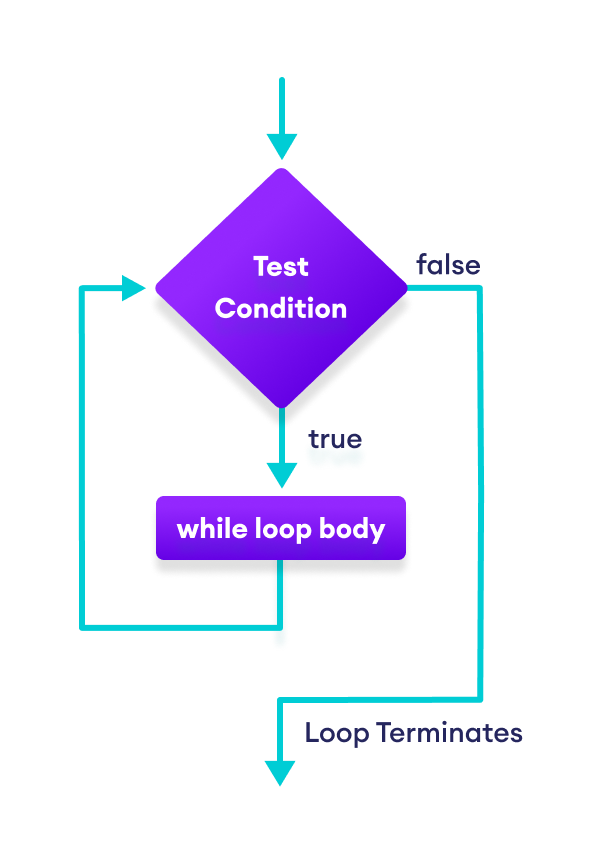
Example 1: Swift while Loop
// program to display numbers from 1 to 5
// initialize the variable
var i = 1, n = 5
// while loop from i = 1 to 5
while (i <= n) {
print(i)
i = i + 1
}
Output
1 2 3 4 5
Here's how the program works.
| Variable | Condition: i <= n |
Action |
|---|---|---|
i = 1n = 5 |
true |
1 is printed. i is increased to 2. |
i = 2n = 5 |
true |
2 is printed. i is increased to 3. |
i = 3n = 5 |
true |
3 is printed. i is increased to 4. |
i = 4n = 5 |
true |
4 is printed. i is increased to 5. |
i = 5n = 5 |
true |
5 is printed. i is increased to 6. |
i = 6n = 5 |
false |
The loop is terminated. |
Example 2: while Loop to Display Game Level
var currentLevel:Int = 0, finalLevel:Int = 5
let gameCompleted = true
while (currentLevel <= finalLevel) {
if gameCompleted {
print("You have passed level \(currentLevel)")
currentLevel += 1
}
}
print("Level Ends")
Output
You have passed level 0 You have passed level 1 You have passed level 2 You have passed level 3 You have passed level 4 You have passed level 5 Level Ends
In the above example, we have used a while loop to check the current level and display it on the console.
repeat...while Loop
The repeat...while loop is similar to while loop with one key difference. The body of repeat...while loop is executed once before the test expression is checked.
The syntax of repeat..while loop is:
repeat {
// body of loop
} while (condition)
Here,
- The body of the loop is executed at first. Then
conditionis evaluated. - If
conditionevaluates totrue, the body of the loop inside therepeatstatement is executed again. conditionis evaluated once again.- This process continues until
conditionevaluates tofalse. Then the loop stops.
Flowchart of repeat...while Loop
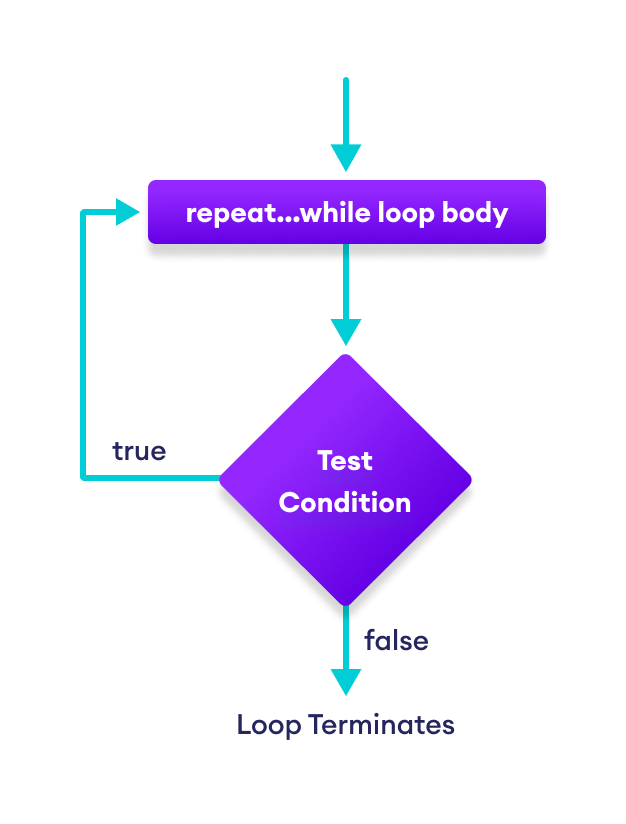
Example 3: repeat...while Loop
// program to display numbers
var i = 1, n = 5
// repeat...while loop from 1 to 5
repeat {
print(i)
i = i + 1
} while (i <= n)
In the above example, initially the value of i = 1 and n = 5. For the first time the statement inside the loop executes without checking the condition. The condition is checked after the first iteration is complete.
Here's how this program works,
| Variable | Condition: i <= n |
Action |
|---|---|---|
i = 1n = 5 |
not checked | 1 is printed. i is increased to 2. |
i = 2n = 5 |
true |
2 is printed. i is increased to 3. |
i = 3n = 5 |
true |
3 is printed. i is increased to 4. |
i = 4n = 5 |
true |
4 is printed. i is increased to 5. |
i = 5n = 5 |
true |
5 is printed. i is increased to 6. |
i = 6n = 5 |
false |
The loop is terminated. |
Infinite while Loop
If the condition of a while loop is always true, the loop runs for infinite times (until the memory is full). This is called infinite while loop. For example,
while (true) {
print("Endless Loop")
}
Output
Endless Loop Endless Loop . . .
Here, the condition is always true. Hence, the while loop will run for infinite times.
for vs while loop
A for-in loop is usually used when the number of iterations is known. For example,
// this loop is iterated 5 times
for number in 1...5 {
// body of loop
}
However, a while loop is usually used when the number of iterations are unknown. For example,
while (condition) {
// body of loop
}
Note: The working of repeat...while is the same as the while. Hence, it is also used when the number of iterations is unknown.