Before we learn about the multidimensional arrays, make sure to know about the single-dimensional array in C#.
In a multidimensional array, each element of the array is also an array. For example,
int[ , ] x = { { 1, 2 ,3}, { 3, 4, 5 } };
Here, x is a multidimensional array which has two elements: {1, 2, 3} and {3, 4, 5}. And, each element of the array is also an array with 3 elements.
Two-dimensional array in C#
A two-dimensional array consists of single-dimensional arrays as its elements. It can be represented as a table with a specific number of rows and columns.
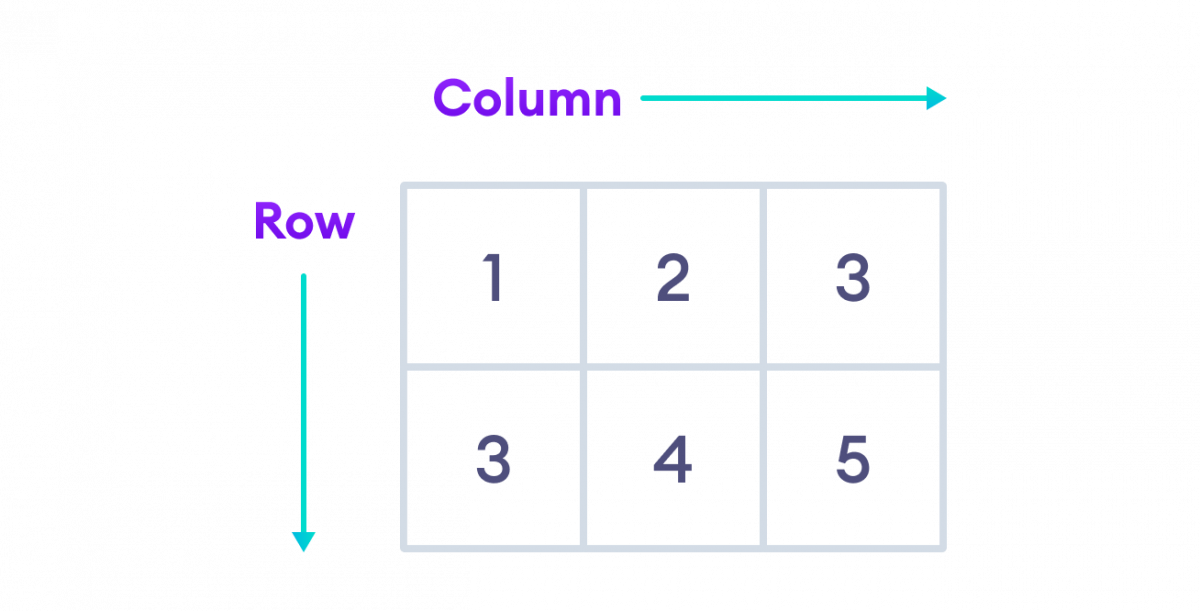
Here, rows {1, 2, 3} and {3, 4, 5} are elements of a 2D array.
1. Two-Dimensional Array Declaration
Here's how we declare a 2D array in C#.
int[ , ] x = new int [2, 3];
Here, x is a two-dimensional array with 2 elements. And, each element is also an array with 3 elements.
So, all together the array can store 6 elements (2 * 3).
Note: The single comma [ , ] represents the array is 2 dimensional.
2. Two-Dimensional Array initialization
In C#, we can initialize an array during the declaration. For example,
int[ , ] x = { { 1, 2 ,3}, { 3, 4, 5 } };
Here, x is a 2D array with two elements {1, 2, 3} and {3, 4, 5}. We can see that each element of the array is also an array.
We can also specify the number of rows and columns during the initialization. For example,
int [ , ] x = new int[2, 3]{ {1, 2, 3}, {3, 4, 5} };
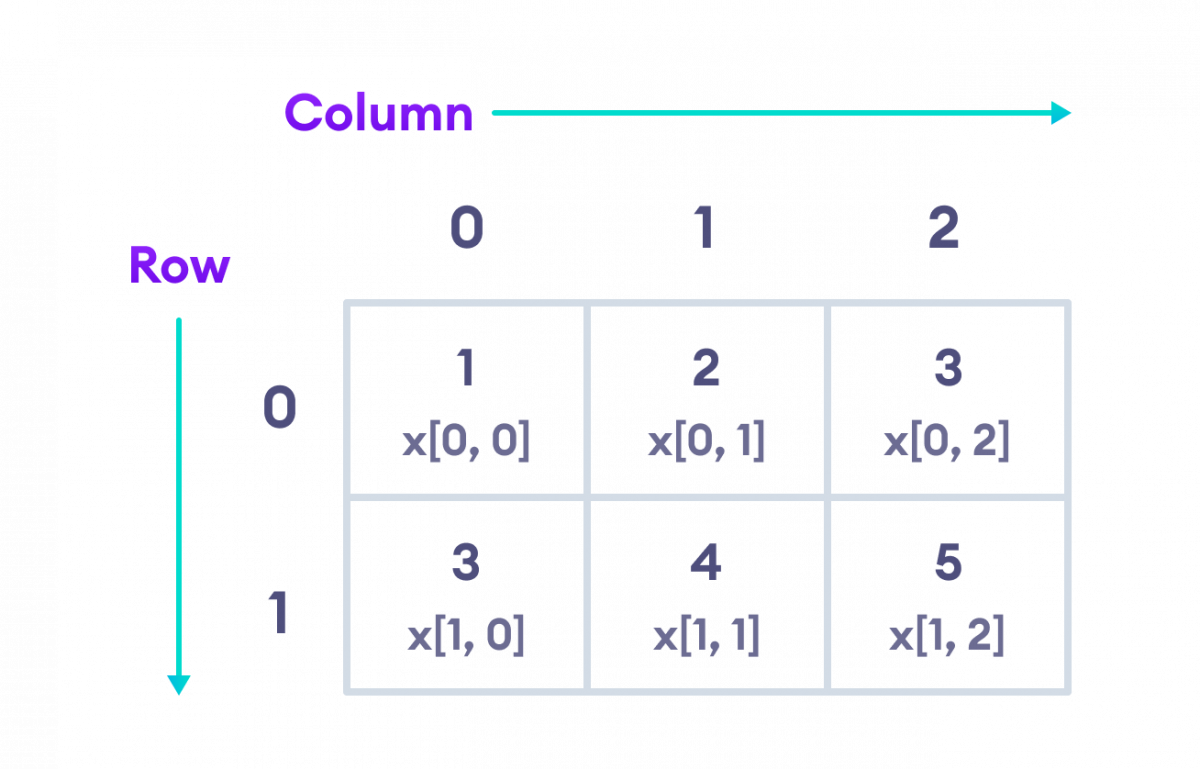
3. Access Elements from 2D Array
We use the index number to access elements of a 2D array. For example,
// a 2D array
int[ , ] x = { { 1, 2 ,3}, { 3, 4, 5 } };
// access first element from first row
x[0, 0]; // returns 1
// access third element from second row
x[1, 2]; // returns 5
// access third element from first row
x[0, 2]; // returns 3
Example: C# 2D Array
using System;
namespace MultiDArray {
class Program {
static void Main(string[] args) {
//initializing 2D array
int[ , ] numbers = {{2, 3}, {4, 5}};
// access first element from the first row
Console.WriteLine("Element at index [0, 0] : "+numbers[0, 0]);
// access first element from second row
Console.WriteLine("Element at index [1, 0] : "+numbers[1, 0]);
}
}
}
Output
Element at index [0, 0] : 2 Element at index [1, 0] : 4
In the above example, we have created a 2D array named numbers with rows {2, 3} and {4, 5}.
Here, we are using the index numbers to access elements of the 2D array.
numbers[0, 0]- access the first element from the first row (2)numbers[1, 0]- access the first element from the second row (4)
Change Array Elements
We can also change the elements of a two-dimensional array. To change the element, we simply assign a new value to that particular index. For example,
using System;
namespace MultiDArray {
class Program {
static void Main(string[] args) {
int[ , ] numbers = {{2, 3}, {4, 5}};
// old element
Console.WriteLine("Old element at index [0, 0] : "+numbers[0, 0]);
// assigning new value
numbers[0, 0] = 222;
// new element
Console.WriteLine("New element at index [0, 0] : "+numbers[0, 0]);
}
}
}
Output
Old element at index [0, 0] : 2 New element at index [0, 0] : 222
In the above example, the initial value at index [0, 0] is 2. Notice the line,
// assigning new value
numbers[0, 0] = 222;
Here, we are assigning a new value 222 at index [0, 0]. Now, the value at index [0, 0] is changed from 2 to 222.
Iterating C# Array using Loop
using System;
namespace MultiDArray {
class Program {
static void Main(string[] args) {
int[ , ] numbers = { {2, 3, 9}, {4, 5, 9} };
for(int i = 0; i < numbers.GetLength(0); i++) {
Console.Write("Row "+ i+": ");
for(int j = 0; j < numbers.GetLength(1); j++) {
Console.Write(numbers[i, j]+" ");
}
Console.WriteLine();
}
}
}
}
Output
Row 0: 2 3 9 Row 1: 4 5 9
In the above example, we have used a nested for loop to iterate through the elements of a 2D array. Here,
numbers.GetLength(0)- gives the number of rows in a 2D arraynumbers.GetLength(1)- gives the number of elements in the row
Note: We can also create a 3D array. Technically, a 3D array is an array that has multiple two-dimensional arrays as its elements. For example,
int[ , , ] numbers = { { { 1, 3, 5 }, { 2, 4, 6 } },
{ { 2, 4, 9 }, { 5, 7, 11 } } };
Here, [ , , ] (2 commas) denotes the 3D array.