The SQL CASE statement evaluates a list of conditions and adds a column with values based on the condition. For example,
-- add a new column 'order_volume' in the Orders table
-- and flag any order greater than 10000 as 'Large Order'
-- and smaller than 10000 as 'Small Order'
SELECT *,
CASE
WHEN amount >= 10000 THEN 'Large Order'
WHEN amount < 10000 THEN 'Small Order'
END AS 'order_volume'
FROM Orders;Here, the result set has a new column, order_volume which labels the rows with amounts greater than or equal to 10000 as Large Order and smaller than 10000 as Small Order.
SQL CASE Syntax
SELECT column1, column2,... ,
CASE
WHEN condition THEN result
END AS alias_name
FROM table;
Here,
- column1,column2, ... are the column names to be included in the result set
CASEchecks theconditionresultis the result or value to be inserted to the new column ifconditionis satisfiedENDends theCASEstatementASspecifies the namealias_namefor the new column- table is the name of the table.
Note: The syntax of CASE always starts with the CASE keyword and ends with the END keyword followed by a column name alias.
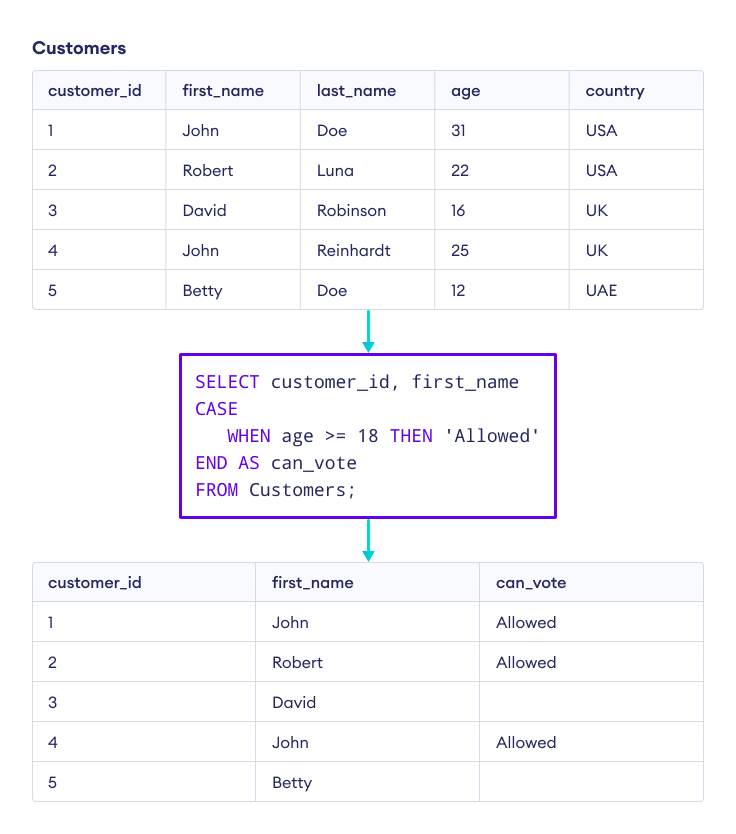
Example: Voter Eligibility Using SQL CASE
-- add a new column 'can_vote' to Customers table
-- insert 'Allowed' into it if customer is older than 17
SELECT customer_id, first_name,
CASE
WHEN age >= 18 THEN 'Allowed'
END AS can_vote
FROM Customers;Here, the SQL command checks each row with the given case. The result set contains:
- values from customer_id and first_name columns
- a new can_vote column with value
Allowedif age is greater than 18, otherwises empty
Example: SQL CASE to Calculate the Discount Amount
Let's take a look at another example where we want to provide a 10% discount on each order for a Christmas sale if the amount is 400 or more.
SELECT order_id, customer_id,
CASE
WHEN amount >= 400 THEN (amount - amount * 10/100)
END AS offer_price
FROM Orders;Here, the CASE statement checks if the amount is greater than or equal to 400. If this condition is satisfied, a new column offer_price will contain the values equal to amount - amount * 10/100.
CASE With Multiple Conditions
It is also possible to stack multiple conditions inside a single CASE clause.
Syntax
SELECT column1, column2, ...
CASE
WHEN condition1 THEN result1
WHEN condition2 THEN result2
-- Add more WHEN conditions and results as needed
END AS alias_name
FROM table_name;
We can add as many WHEN ... THEN conditions as required in the CASE statement. For example,
-- multiple CASE conditions in SQL
SELECT customer_id, first_name,
CASE
WHEN country = 'USA' THEN 'United States of America'
WHEN country = 'UK' THEN 'United Kingdom'
END AS country_name
FROM Customers;Here, the result set contains a new column, country_name along with customer_id and first_name.
The value of country_name becomes:
- United States of America if the country is equal to USA
- United Kingdom if the country is equal to UK
CASE With ELSE
A CASE statement can have an optional ELSE clause. The ELSE clause is executed if none of the conditions in the CASE statement is matched.
Syntax
SELECT customer_id, first_name,
CASE
WHEN condition1 THEN result1
WHEN condition2 THEN result2
-- Add more WHEN conditions and results as needed
ELSE else_result
END AS alias_name
FROM table_name;
The ELSE clause has no condition as it is executed if none of the WHEN conditions are matched. For example,
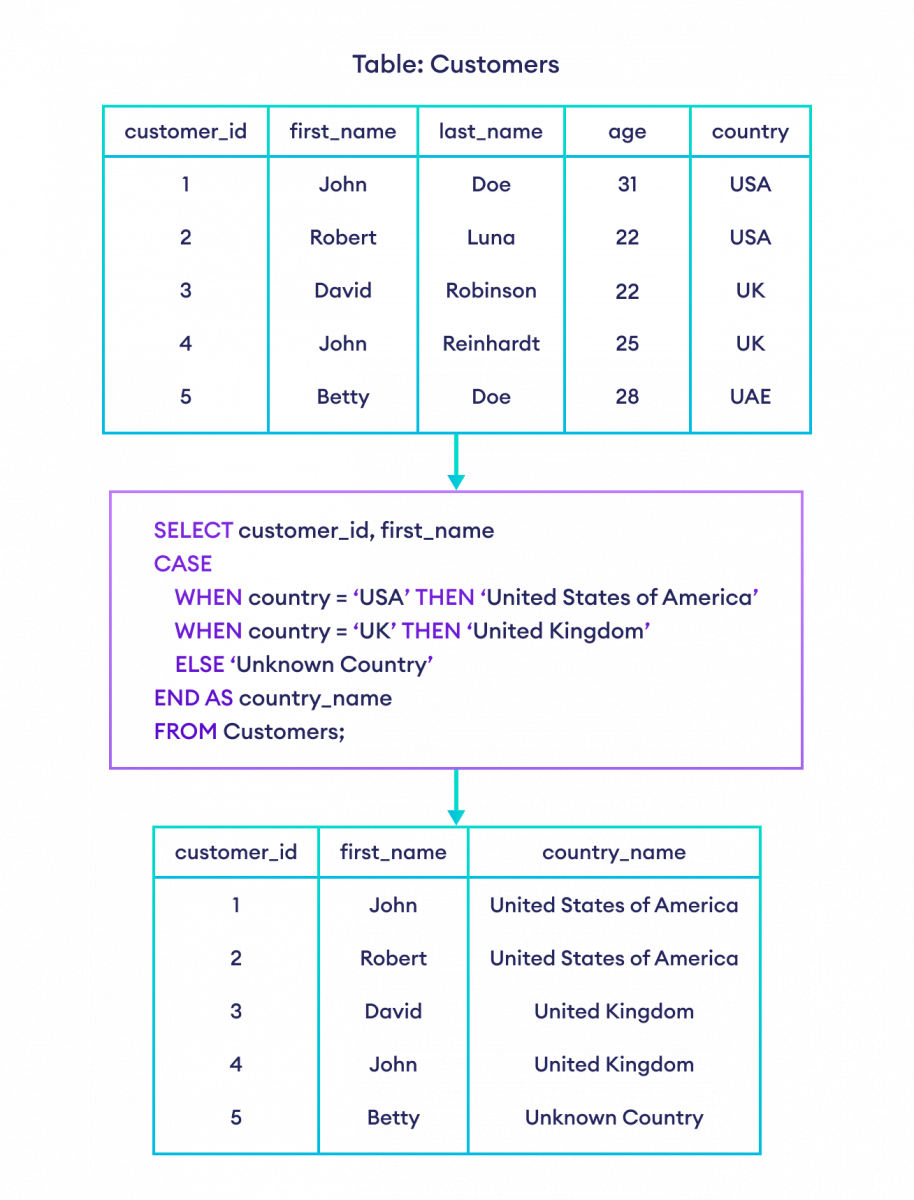
-- CASE condition with ELSE clause in SQL
SELECT customer_id, first_name,
CASE
WHEN country = 'USA' THEN 'United States of America'
WHEN country = 'UK' THEN 'United Kingdom'
ELSE 'Unknown Country'
END AS country_name
FROM Customers;Here, the result set contains a new column, country_name along with customer_id and first_name.
The value of country_name becomes:
- United States of America if country is USA
- United Kingdom if country is UK
- Unknown Country if country is neither USA nor UK (because of the
ELSEclause).