The SQL JOIN statement is used to combine rows from two tables based on a common column and selects records that have matching values in these columns.
Example
-- join the Customers and Orders tables
-- based on the common values of their customer_id columns
SELECT Customers.customer_id, Customers.first_name, Orders.item
FROM Customers
JOIN Orders
ON Customers.customer_id = Orders.customer_id;Here, the SQL command joins the Customers and Orders tables based on the common column, customer_id of both tables.
The result set will consist of
customer_idandfirst_namecolumns from theCustomerstableitemcolumn from theOrderstable
SQL JOIN Syntax
SELECT columns_from_both_tables
FROM table1
JOIN table2
ON table1.column1 = table2.column2
Here,
- table1 and table2 are the two tables that are to be joined
- column1 is the column in table1 that is related to column2 in table2
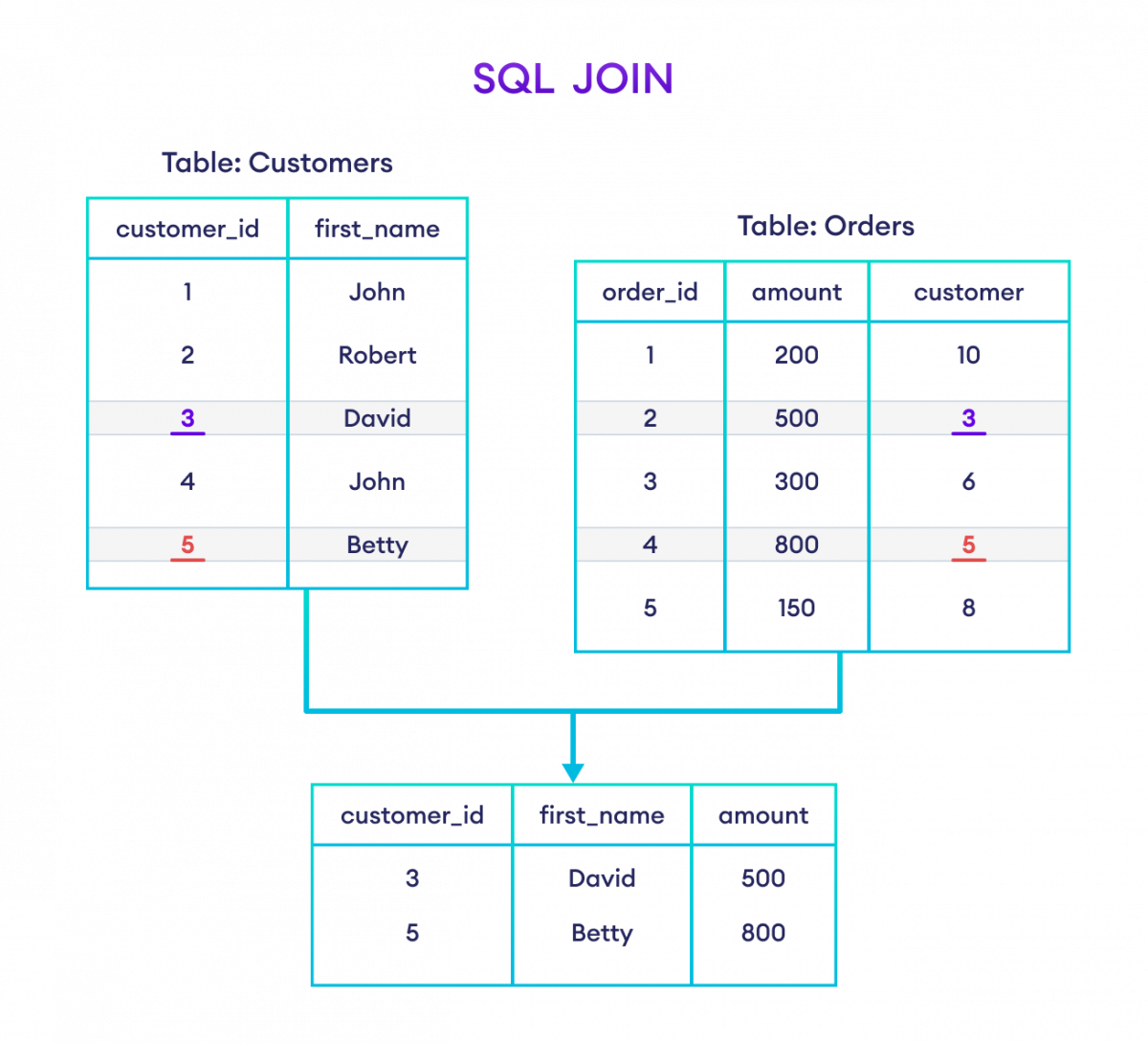
Example: Join Two Table Based on Common Column
-- join Customers and Orders tables based on
-- customer_id of Customers and customer column of Orders
SELECT Customers.customer_id, Customers.first_name, Orders.amount
FROM Customers
JOIN Orders
ON Customers.customer_id = Orders.customer;Here, the SQL command selects the columns:
-
customer_idandfirst_namefrom theCustomerstable -
amountfrom theOrderstable
The result set will contain those values where there is a match between customer_id (of the Customers table) and customer (of the Orders table).
JOIN Multiple Tables
We can also join more than two tables using JOIN. For example,
-- join three tables: Customers, Orders, and Shippings
SELECT Customers.first_name, Orders.item, Shippings.status
FROM Customers
JOIN Orders ON Customers.customer_id = Orders.customer_id
JOIN Shippings ON Customers.customer_id = Shippings.customer;This SQL command joins three tables and selects relevant columns from each, based on the matching customer_id.
Note: To learn more about how to join multiple tables, visit SQL Join Multiple Tables.
Types of SQL JOINs
In SQL, we have four main types of joins:
More on SQL JOIN
In SQL, the Self JOIN operation allows us to join a table with itself, creating a relationship between rows within the same table.
Let's look at an example.
SELECT
C1.first_name AS FirstPerson,
C2.first_name AS SecondPerson,
C1.country
FROM Customers C1, Customers C2
WHERE C1.country = C2.country AND C1.first_name != C2.first_name;
The SQL query will return pairs of customers who are from the same country but have different first names.
To learn more, Visit SQL Self JOIN.
We can use AS aliases with table names to make our query short and clean. For example,
-- use alias C for Customers table
-- use alias O for Orders table
SELECT C.customer_id, C.first_name, O.amount
FROM Customers AS C
JOIN Orders AS O
ON C.customer_id = O.customer;
Here, the SQL command joins the Customers and Orders tables while assigning the aliases C and O to them, respectively.
Also, we can change the column names temporarily using AS aliases. For example,
-- use alias C for Customers table
-- use alias O for Orders table
SELECT C.customer_id AS cid, C.first_name AS name, O.amount
FROM Customers AS C
JOIN Orders AS O
ON C.customer_id = O.customer;
Apart from giving aliases to the tables, the SQL command above also assigns aliases to the columns of the Customers table:
customer_idcolumn has the aliascidfirst_namecolumn has the aliasname
Here's an example of JOIN with the WHERE clause:
-- join Customers and Orders table with matching fields customer_id and customer
SELECT Customers.customer_id, Customers.first_name, Orders.amount
FROM Customers
JOIN Orders
ON Customers.customer_id = Orders.customer
WHERE Orders.amount >= 500;
Here, the SQL command joins two tables and selects rows where the amount is greater than or equal to 500.