A wildcard character in SQL is used with the LIKE clause to replace a single character or a set of characters in a string.
% and _ are two commonly used wildcard characters in SQL.
Example
-- select customers who live in countries
-- that start with 'US' followed by a single character
SELECT *
FROM Customers
WHERE country LIKE 'US_'Here, _ is a wildcard character that represents exactly one character after a string.
So, the SQL query selects customers whose country starts with US and ends with a single character after it.
SQL Wildcard Syntax
The syntax of SQL Wildcards is:
SELECT column1, column 2, ...
FROM table
WHERE column LIKE 'Wildcard String';
Here,
column1, column2, ...are the columns to select the data fromtableis the name of the tablecolumnis the column we want to apply the filter toLIKEmatches thecolumnwithWildcard StringWildcard Stringis a combination of strings and wildcard characters
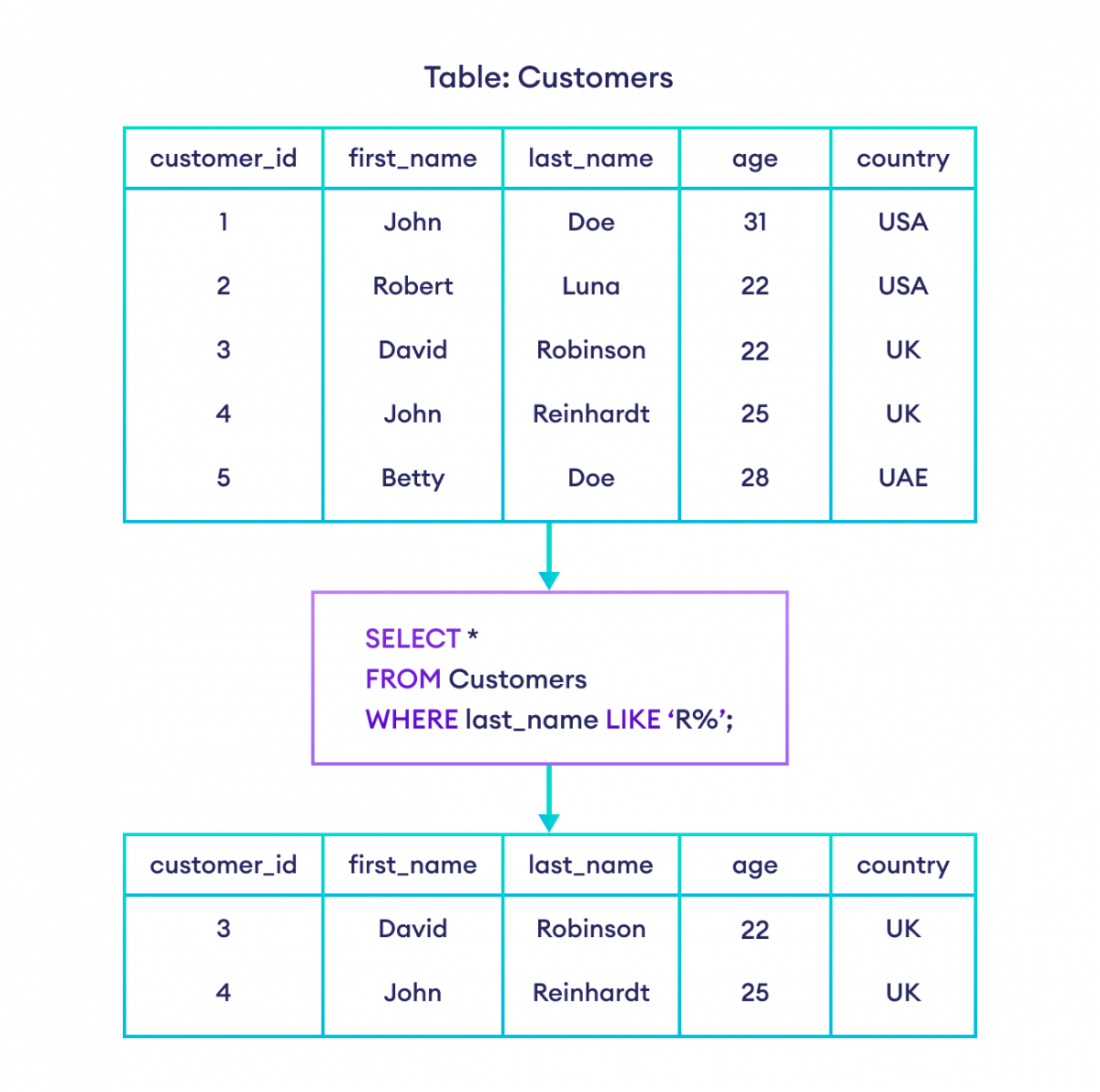
For example,
-- select rows where the last name
-- of customers start with R
SELECT *
FROM Customers
WHERE last_name LIKE 'R%';Here, % (zero or more characters) is a wildcard. So, the SQL command selects customers whose last_name starts with R followed by zero or more characters after it.
Recommended Reading: SQL LIKE Operator
% Wildcard in SQL
The % wildcard in SQL is used to represent zero or more characters. For example,
-- select rows where the first names
-- of customers start with J
SELECT *
FROM Customers
WHERE first_name LIKE 'J%';Here, the SQL command selects customers whose last name starts with J followed by zero or more characters.
| Expression | String | Matched? |
|---|---|---|
J% |
JJarMajorMajority |
match match no match no match |
_ Wildcard in SQL
The _ wildcard in SQL is used to represent exactly one character in a string. For example,
-- select customers whose countries start with U
-- followed by a single character
SELECT *
FROM Customers
WHERE country LIKE 'U_';Here, the SQL command selects customers whose country name starts with U and is followed by only one character.
| Expression | String | Matched? |
|---|---|---|
U_ |
UUKUSA |
no match match no match |
[] Wildcard in SQL
The [] wildcard in SQL is used to represent any one character inside brackets. For example,
-- select customers with country that starts with UK or UA
-- and is followed by any number of characters
SELECT *
FROM Customers
WHERE country LIKE 'U[KA]%';
Here, the SQL command selects customers whose country name starts with U and is followed by either K or A and any number of characters afterward.
| Expression | String | Matched? |
|---|---|---|
U[KA]% |
UUKUAEUSA |
no match match match no match |
! Wildcard in SQL
The ! wildcard in SQL is used to exclude characters from a string. For example,
--select rows where customer's last names don't start with D or R
SELECT *
FROM Customers
WHERE last_name LIKE '[!DR]%';
Here, the SQL command selects customers whose last_name does not start with D or R.
| Expression | String | Matched? |
|---|---|---|
[!DR]% |
DoeReinhardtLunaDOR |
no match no match match no match match no match |
Wildcard Characters in Different Databases
%- zero or more characters_- single character[]- single character within the brackets^- any character not within the brackets-- single character within a range
%- zero or more characters_- single character
%- zero or more characters_- single character[]- single character within the brackets{}- escaped character