We use the IN operator with the WHERE clause to match values in a list.
Example
-- select customers from the USA
SELECT first_name, country
FROM Customers
WHERE country IN ('USA');Here, the SQL command selects rows from the Customers table whose country value is 'USA'.
SQL IN Syntax
SELECT column1, column2, ...
FROM table
WHERE column IN (value1, value2, ...);
Here,
column1, column2, ...are the table columns.tableis the table name from where we select the data.columnis where the values are compared against.INoperator specifies values that thecolumnvalue should be compared against.value1, value2, ...are the values thecolumnvalue is compared against.
Example: SQL IN
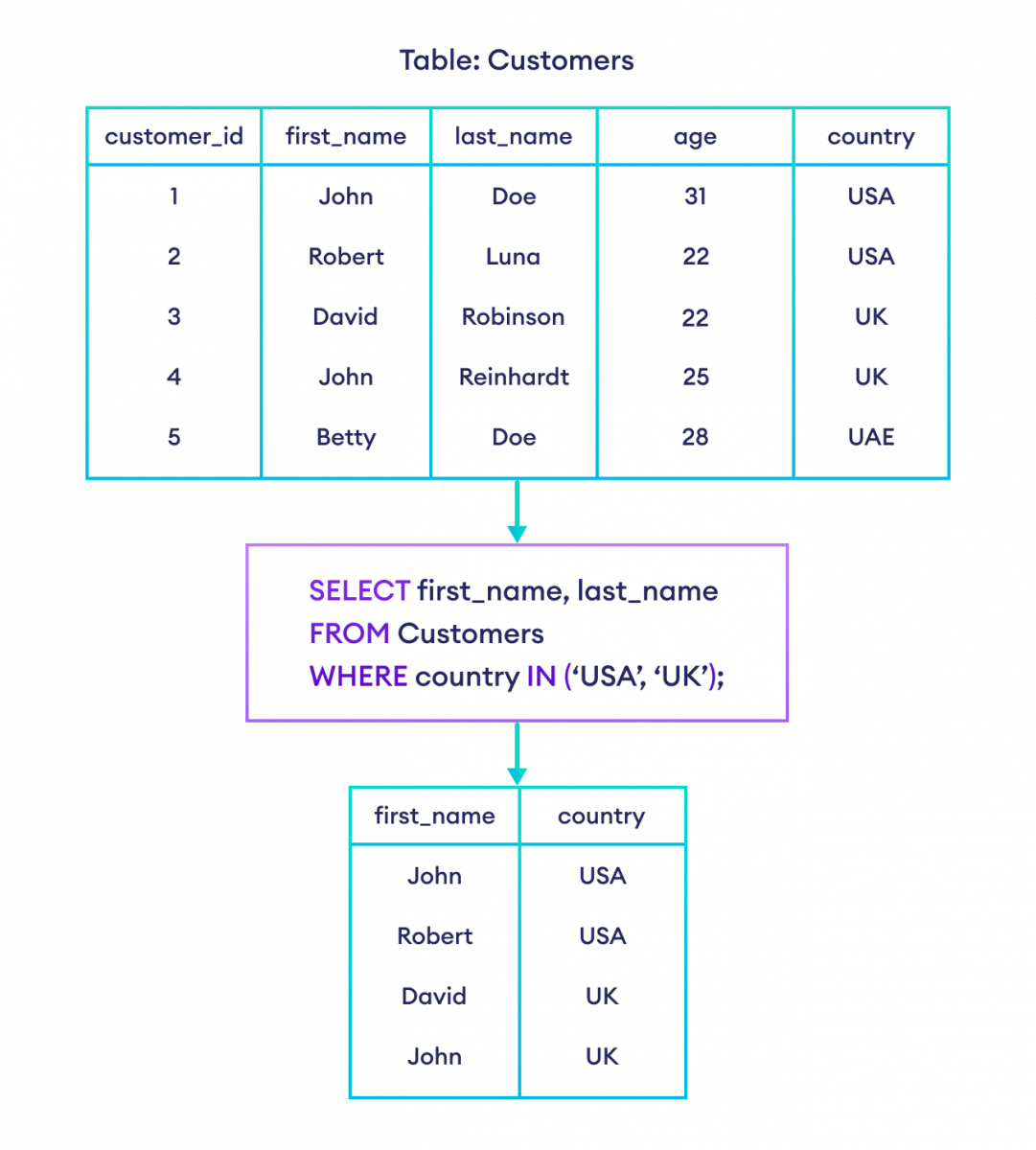
-- select rows if the country is either USA or UK
SELECT first_name, country
FROM Customers
WHERE country IN ('USA', 'UK');Here, the SQL command selects rows if the country is either the USA or the UK.
Example: IN Operator to Select Rows Based on Country Value
The IN operator can be used to choose rows where a specific value is present in the specified field.
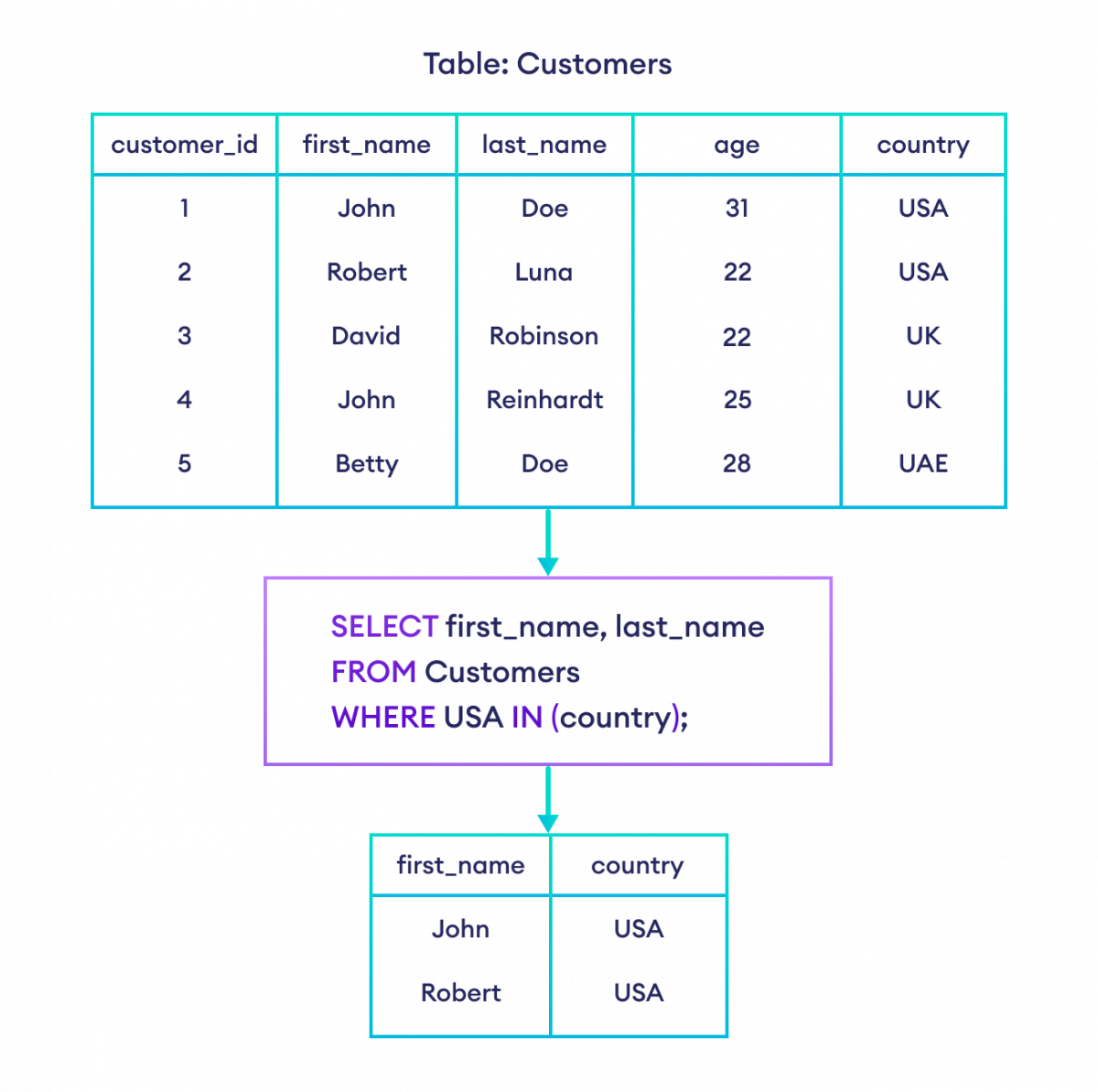
-- select rows with value 'USA' in the country column
SELECT first_name, country
FROM Customers
WHERE 'USA' IN (country);Here, the SQL command selects the rows if the USA value exists in the country field.
SQL NOT IN Operator
The NOT IN operator excludes the rows that match values in the list. It returns all the rows except the excluded rows.
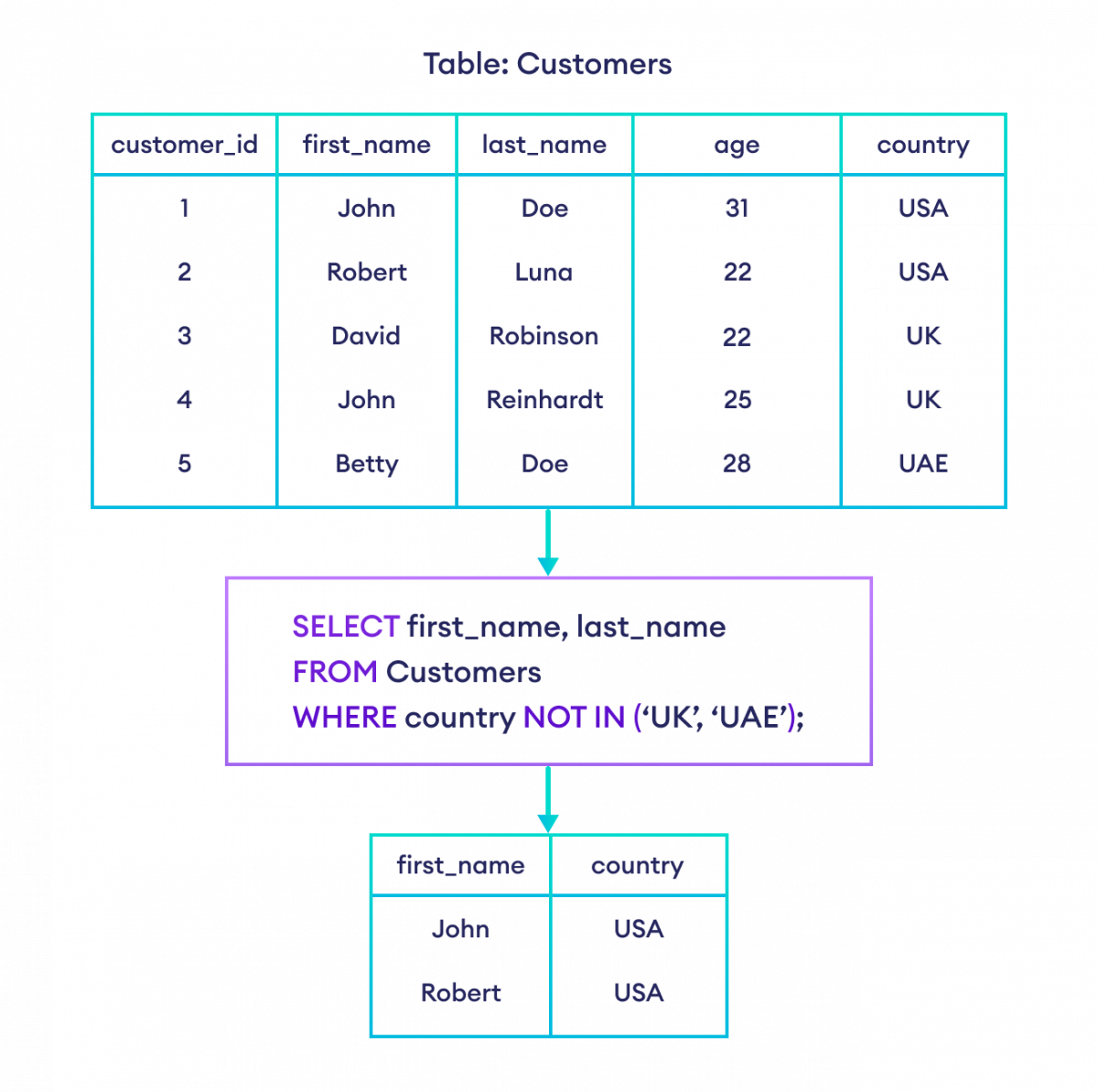
-- select rows where country is not in UK or UAE
SELECT first_name, country
FROM Customers
WHERE country NOT IN ('UK', 'UAE');Here, the SQL command selects rows if the UK or UAE is not in the country column.
Note: The working of the IN operator is reversed by the NOT Operator. They are basically two operators combined. To learn more, visit SQL AND, OR, and NOT Operators.
More on SQL IN
The IN operator ignores duplicate values in the list. For example,
-- IN ignores the duplicate 'USA' value
SELECT first_name, country
FROM Customers
WHERE country IN ('USA', 'UK', 'USA');
The code above is equivalent to the one below.
-- select customers that live in either the USA or the UK
SELECT first_name, country
FROM Customers
WHERE country IN ('USA', 'UK');
Suppose we only want the details of those customers who have placed an order.
Here's how we can do that using a subquery.
-- select only those customers who have placed an order
-- the subquery is enclosed within parentheses after the IN keyword
SELECT customer_id, first_name
FROM Customers
WHERE customer_id IN (
SELECT customer_id
FROM Orders
);
Here, the SQL command
- selects customer_id from the Orders table using the subquery,
- selects rows from the Customers table where customer_id is in the result set of the subquery i.e., if the customer_id is also in the Orders table.
To learn more, visit SQL Subquery.
Also Read: