The SQL EXISTS operator tests the existence of any value in a subquery i.e. it executes the outer SQL query only if the subquery is not NULL (empty result-set).
Example
-- select customer id and first name of customers
-- whose order amount is less than 12000
SELECT customer_id, first_name
FROM Customers
WHERE EXISTS (
SELECT order_id
FROM Orders
WHERE Orders.customer_id = Customers.customer_id AND amount < 12000
);Here, the SQL query:
- checks for the order_id of customers in the Orders table where amount is less than 12000
- returns the customer_id and first_name of customers from the Customers table who have made a purchase of less than 12000
SQL Exists Syntax
The syntax of the SQL EXISTS operator is:
SELECT column1, column2, ...
FROM table
WHERE EXISTS(SUBQUERY);
Here,
column1, column2, ...are the column names to filtertablerefers to the name of the tableEXISTStests the result of the subquerySUBQUERYcan be any SQL query
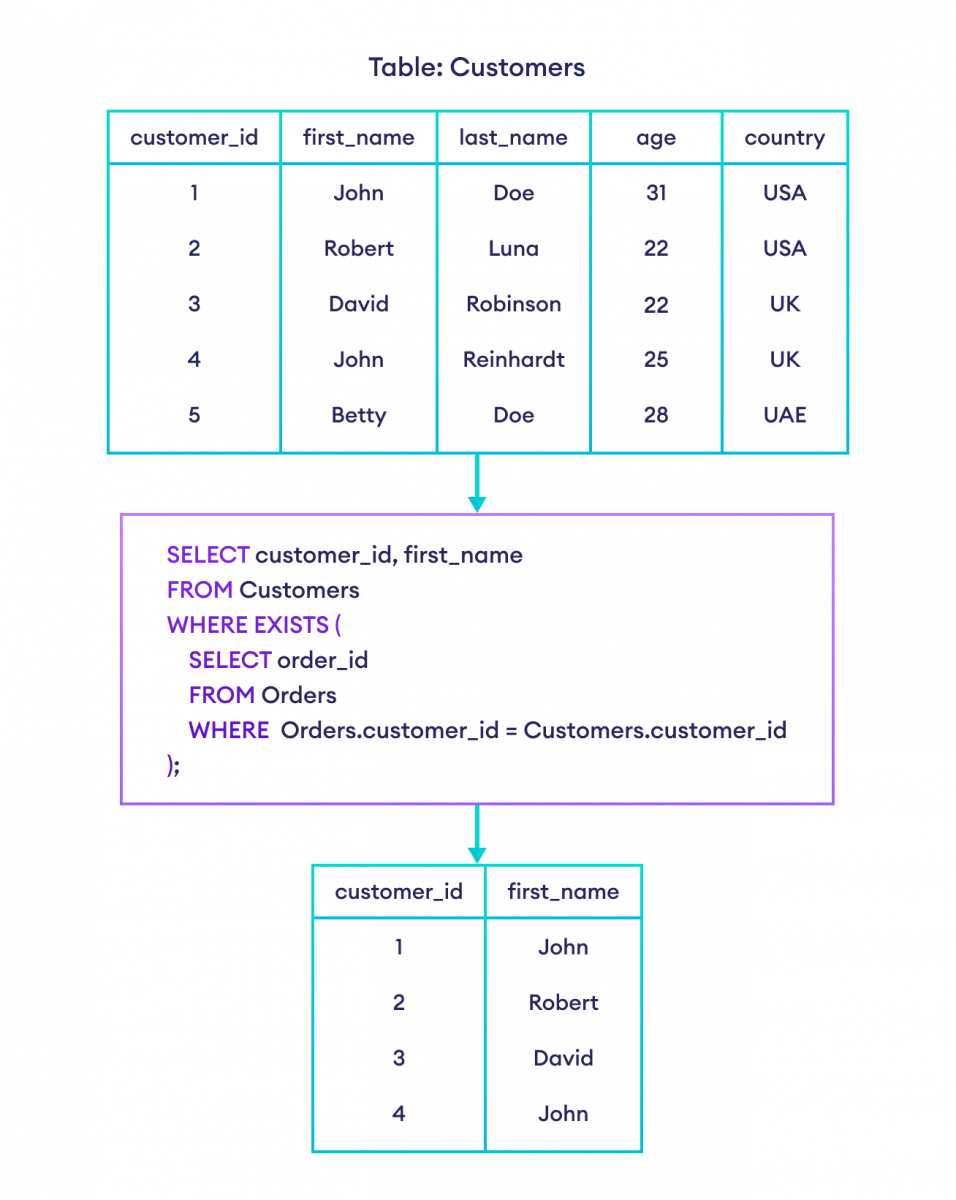
Example 1: SQL Exists
-- select customer id and first name of customers from Customers table
-- if the customer id exists in the Orders table
SELECT customer_id, first_name
FROM Customers
WHERE EXISTS (
SELECT order_id
FROM Orders
WHERE Orders.customer_id = Customers.customer_id
);Here is how the SQL command works:
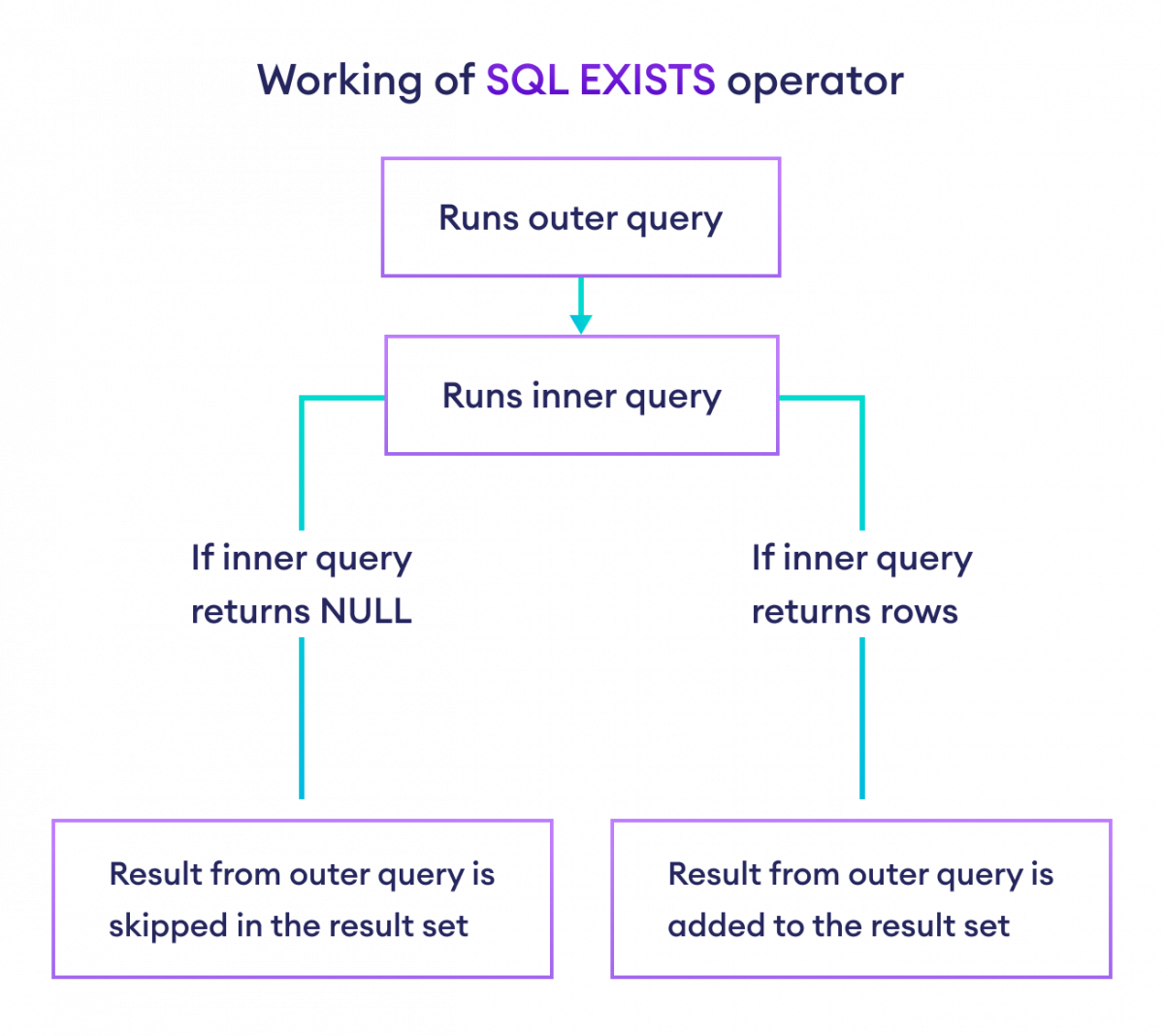
This process is repeated for each row of the outer query.
SQL NOT EXISTS
We can also use the NOT operator to inverse the working of the EXISTS clause. The SQL command executes if the subquery returns an empty result-set.
For example,
-- select customer id and first name from Customers table
-- if the customer id doesn't exist in the Orders table
SELECT customer_id, first_name
FROM Customers
WHERE NOT EXISTS (
SELECT order_id
FROM Orders
WHERE Orders.customer_id = Customers.customer_id
);Here, the SQL command returns a row from the Customers table if the related row is not in the Orders table.
SQL EXISTS Examples
We can add an optional IF EXISTS command with the DROP TABLE clause. For example,
DROP TABLE IF EXISTS my_table;
We can add an optional IF NOT EXISTS command with the CREATE TABLE clause. For example,
-- create a table if it doesn't exist
CREATE TABLE IF NOT EXISTS Companies (
id int,
name varchar(50),
address text,
email varchar(50),
phone varchar(10)
);
The SQL query below selects orders from the Orders table for customers who are older than 23 years.
SELECT *
FROM Orders
WHERE EXISTS (
SELECT customer_id
FROM Customers
WHERE Orders.customer_id = Customers.customer_id
AND Customers.age > 23
);
Also Read: