In SQL, the DELETE clause is used to delete row(s) from a database table.
Example
DELETE FROM Customers
WHERE customer_id = 4;Here, the SQL command will delete a row from the Customers table if its customer_id is 4.
DELETE Syntax
The syntax of the SQL DELETE command is:
DELETE FROM table_name
[WHERE condition];
Here,
table_nameis the name of the table from which rows are to be deletedconditionspecifies which rows should be deleted[]indicates that theWHEREclause is optional.
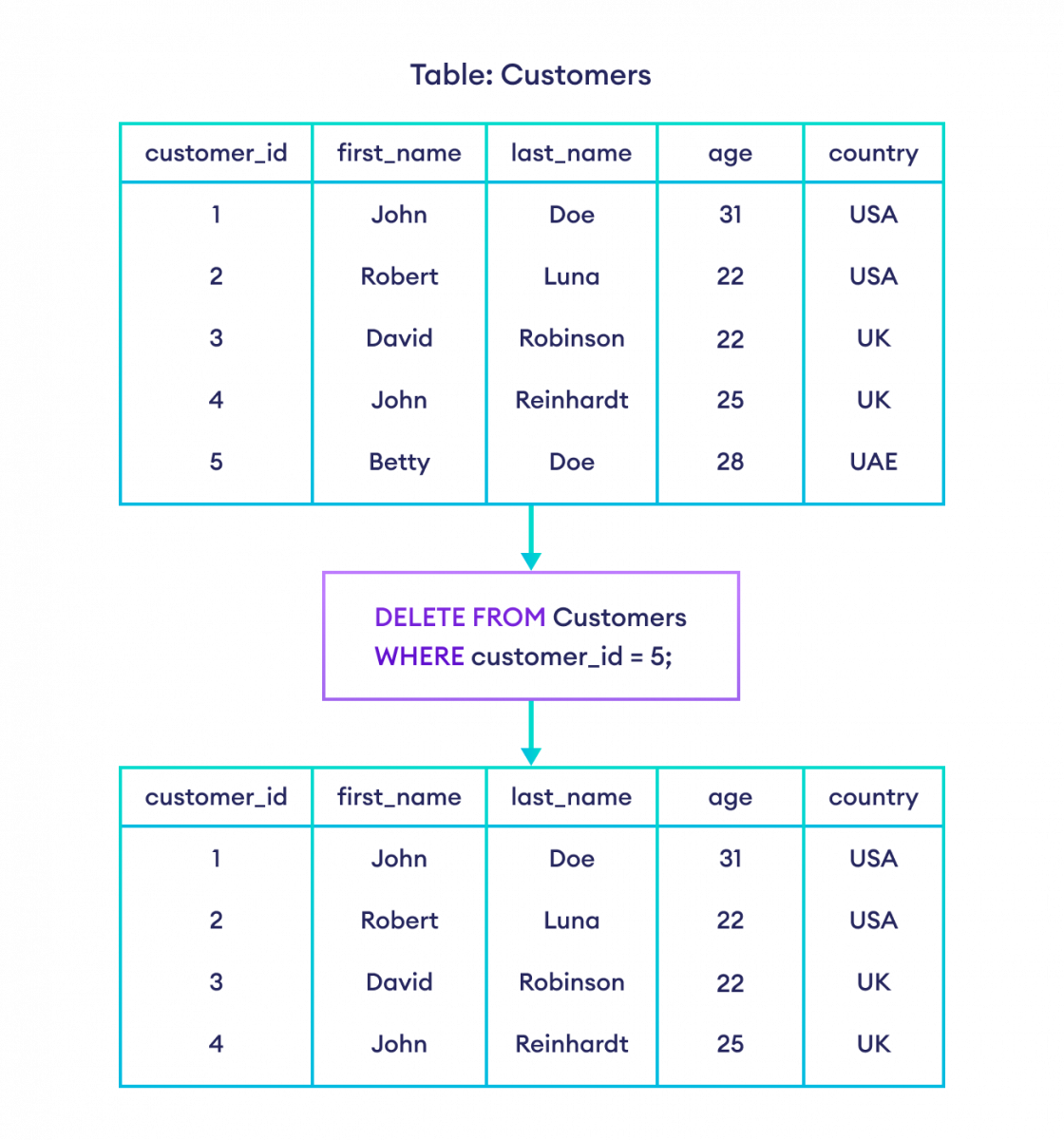
Delete a Single Row in a Table
We can delete a single row in a table using the DELETE command. For example,
DELETE FROM Customers
WHERE customer_id = 5;Here, the SQL command will delete a row from the Customers table if its customer_id is 5.
Delete all Rows in a Table
The WHERE clause determines which rows to delete. However, we can delete all rows at once if we omit the WHERE clause. For example,
DELETE FROM Customers;Here, the SQL command deletes all rows from the Customers table.
Note: Be careful when you use DELETE. Records may be lost permanently if the database is not backed up.
Truncate Table in SQL
The TRUNCATE TABLE clause is another way to delete all rows from a table at once. For example,
TRUNCATE TABLE Customers;
Here, the SQL command deletes all rows from the Customers table.
Note: This command is not supported by our SQL online editor as it is based on SQLite.
SQL DELETE vs. TRUNCATE
| SQL DELELTE | SQL TRUNCATE |
|---|---|
SQL DELETE supports the WHERE clause. |
SQL TRUNCATE doesn't support the WHERE clause. |
SQL DELETE can remove single, multiple, or all rows/records from a table. |
SQL TRUNCATE can only remove all the records from a table. |