We use the SQL LIKE operator with the WHERE clause to get a result set that matches the given string pattern.
Example
-- select customers who live in the UK
SELECT first_name
FROM Customers
WHERE country LIKE 'UK';Here, the SQL command selects the first name of customers whose country is UK.
SQL LIKE Syntax
SELECT column1, column2, ...
FROM table
WHERE column LIKE value;
Here,
column1,column2, ...are the columns to select the data fromtableis the name of the tablecolumnis the column we want to apply the filter toLIKEmatches thecolumnwithvaluevalueis the pattern you want to match in the specifiedcolumn
Example: SQL LIKE
-- select customers who live in the UK
SELECT *
FROM Customers
WHERE country LIKE 'UK';Here, the SQL command selects customers whose country is UK.
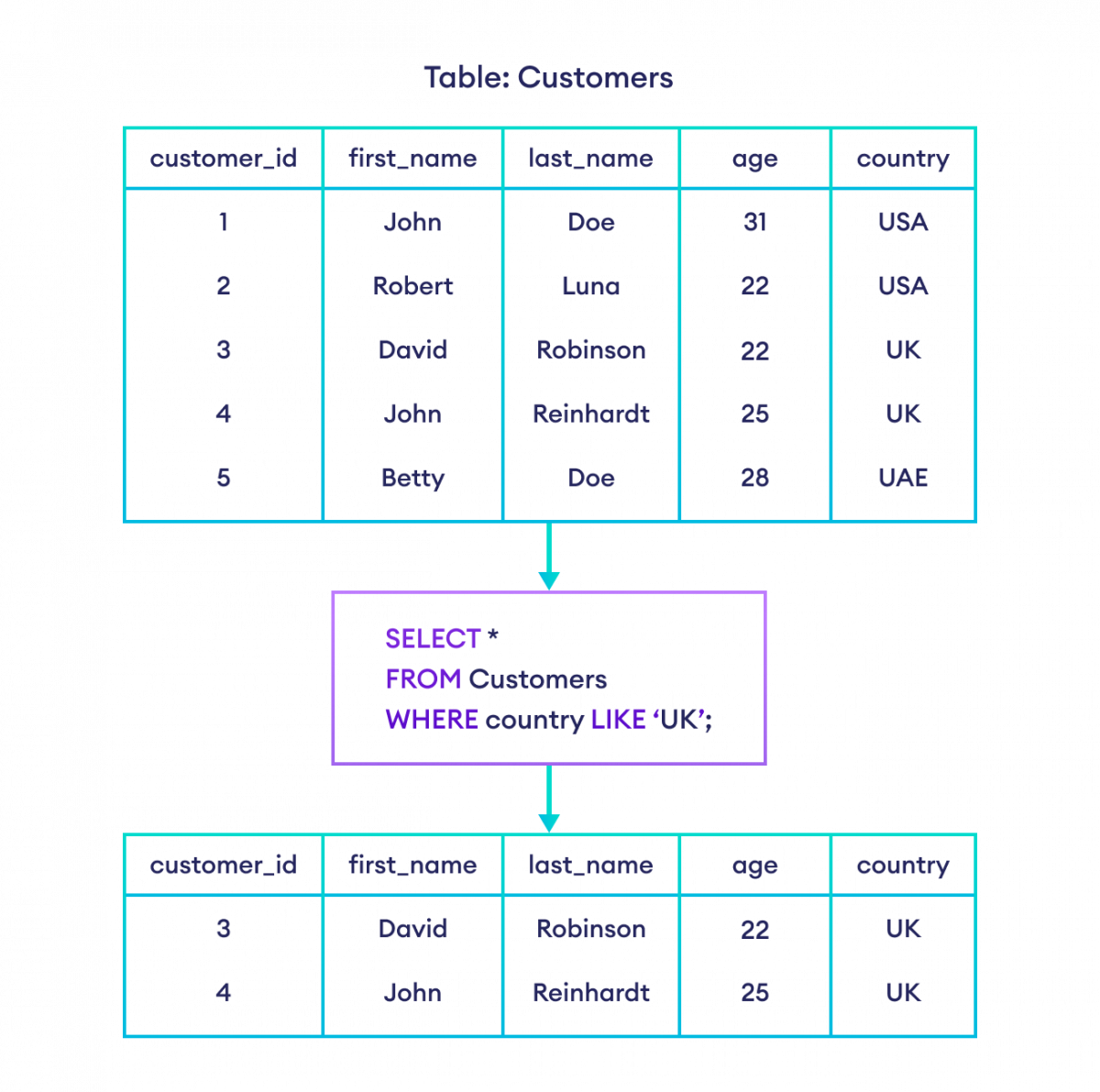
Note: Although the LIKE operator behaves similarly to the = operator in this example, they are not the same. The = operator is used to check equality, whereas the LIKE operator is used to match string patterns only.
SQL LIKE With Wildcards
% Wildcard
The SQL LIKE query is often used with the % wildcard to match a pattern of a string. For example,
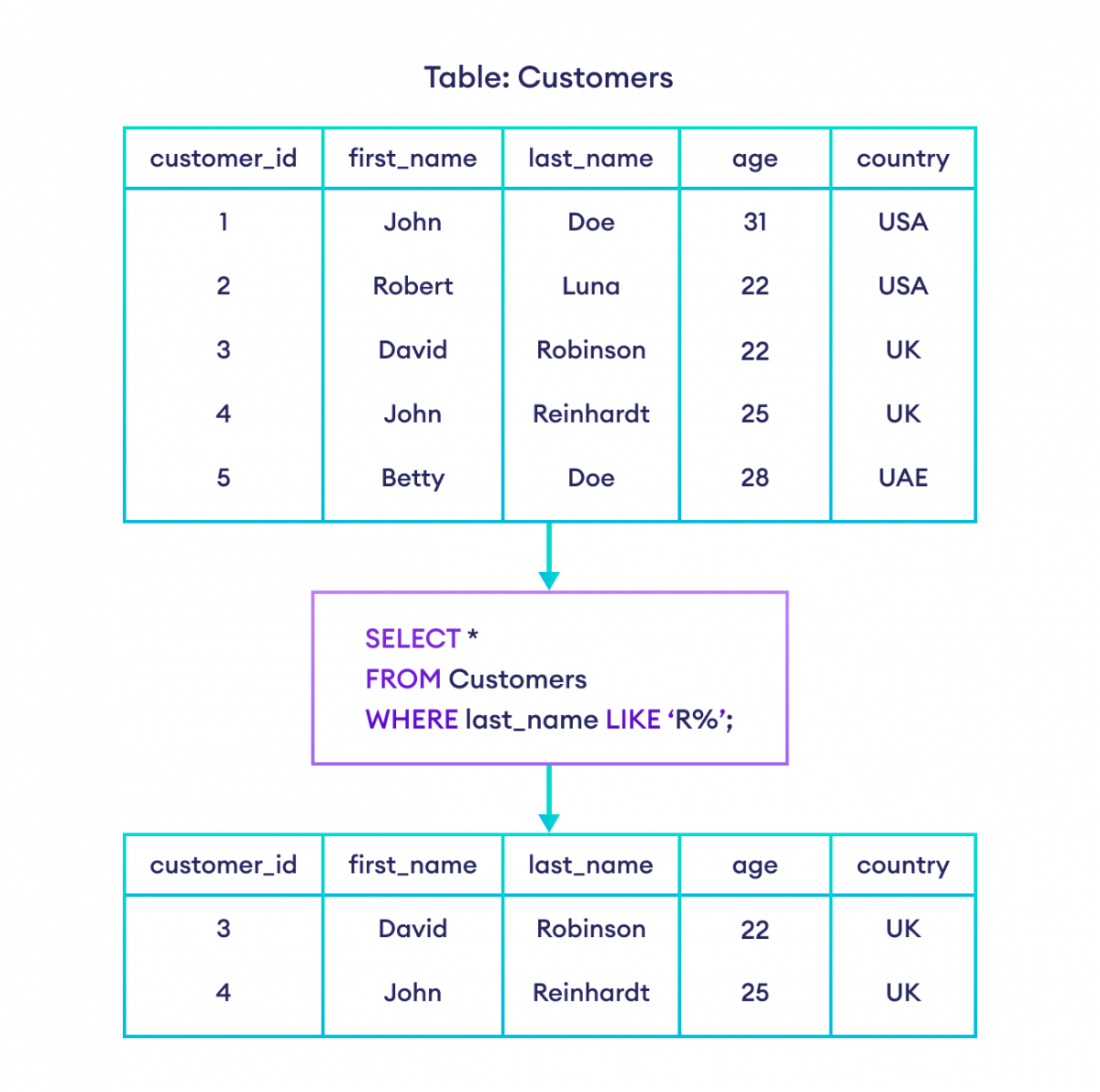
-- select customers whose
-- last name starts with R
SELECT *
FROM Customers
WHERE last_name LIKE 'R%';
Here, % is a wildcard character. Hence, the SQL command selects customers whose last_name starts with R followed by zero or more characters after it.
_ Wildcard
There are more wildcard characters we can use with LIKE.
Let's look at an example using the _ wildcard character.
-- select customers whose
-- country names start with U
-- followed by a single character
SELECT *
FROM Customers
WHERE country LIKE 'U_';
Here, the SQL command selects customers whose country name starts with U followed by exactly one character.
SQL NOT LIKE Operator
We can also invert the working of the LIKE operator by using the NOT operator with it. This returns a result set that doesn't match the given string pattern.
Syntax
SELECT column1, column2, ...
FROM table_name
WHERE column NOT LIKE value;
Here,
column1,column2, ...are the columns to select the data fromtable_nameis the name of the tablecolumnis the column we want to apply the filter toNOT LIKEignores the match of thecolumnwith thevaluevalueis the pattern you don't want to match in the specifiedcolumn
For example,
-- select customers who don't live in the USA
SELECT *
FROM Customers
WHERE country NOT LIKE 'USA';Here, the SQL command selects all customers except those whose country is USA.
SQL LIKE With Multiple Values
We can use the LIKE operator with multiple string patterns using the OR operator. For example,
-- select customers whose last_name starts with R and ends with t
-- or customers whose last_name ends with e
SELECT *
FROM Customers
WHERE last_name LIKE 'R%t' OR last_name LIKE '%e';Here, the SQL command selects customers whose last_name starts with R and ends with t or customers whose last_name ends with e.
Also Read: