The SQL SELECT statement is used to select (retrieve) data from a database table.
Example
-- select first_name from Customers table
SELECT first_name
FROM Customers;The above SQL query selects the first_name of all the customers from the Customers table.
SQL SELECT Syntax
The syntax of the SQL SELECT statement is:
SELECT column1, column2, ...
FROM table;
Here,
column1, column2, ...are the table columnstableis the table name from where we select the data
For example,
-- select first_name and last_name columns from Customers table
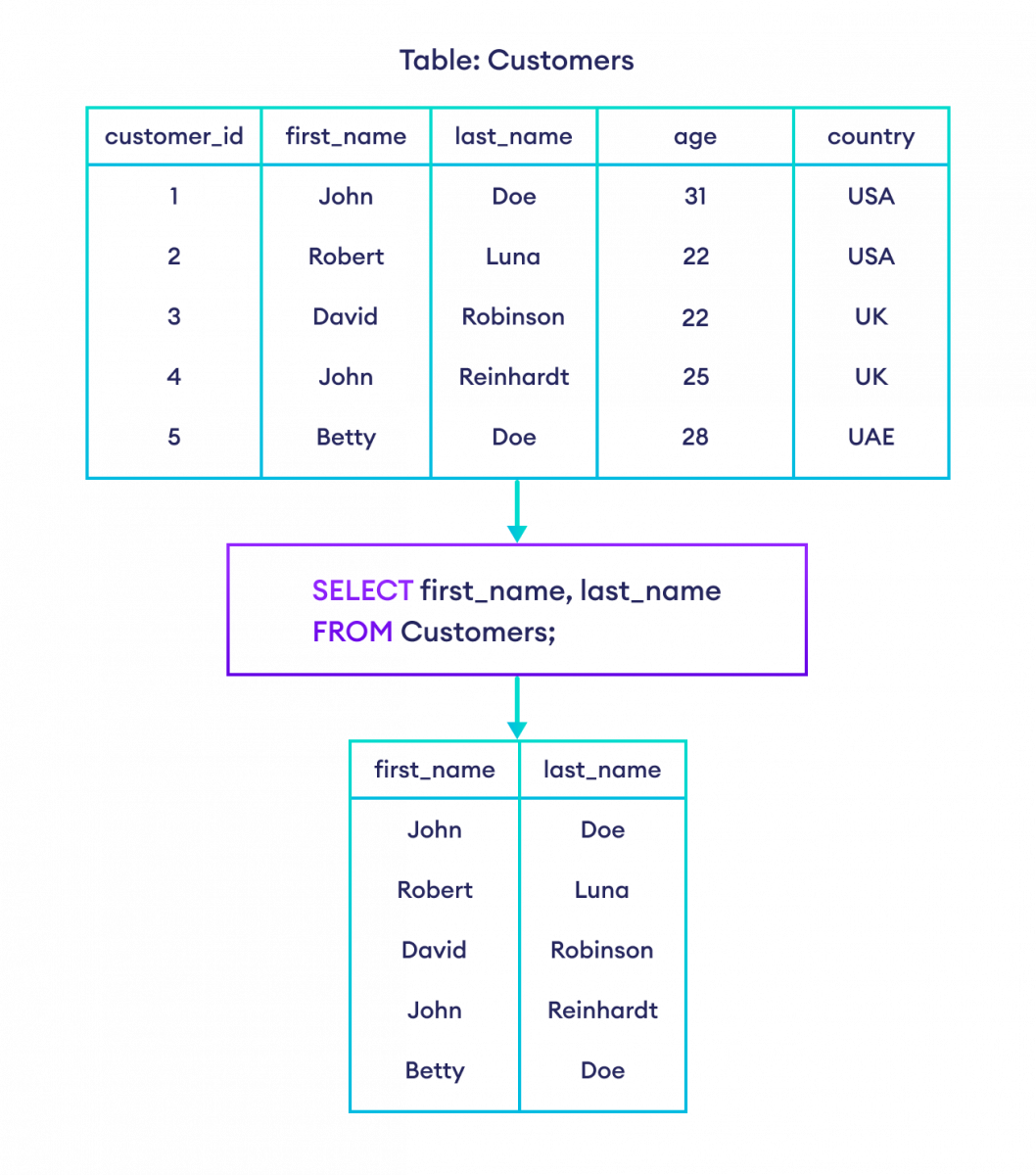
SELECT first_name, last_name
FROM Customers;Here, the SQL command selects the first_name and last_name of all customers in the Customers table.
SQL SELECT ALL
To select all columns from a database table, we use the * character. For example,
-- select all columns from Customers table
SELECT *
FROM Customers;Here, the SQL command selects all columns of the Customers table.

SQL SELECT WHERE Clause
A SELECT statement can have an optional WHERE clause. The WHERE clause allows us to fetch records from a database table that matches specified condition(s). For example,
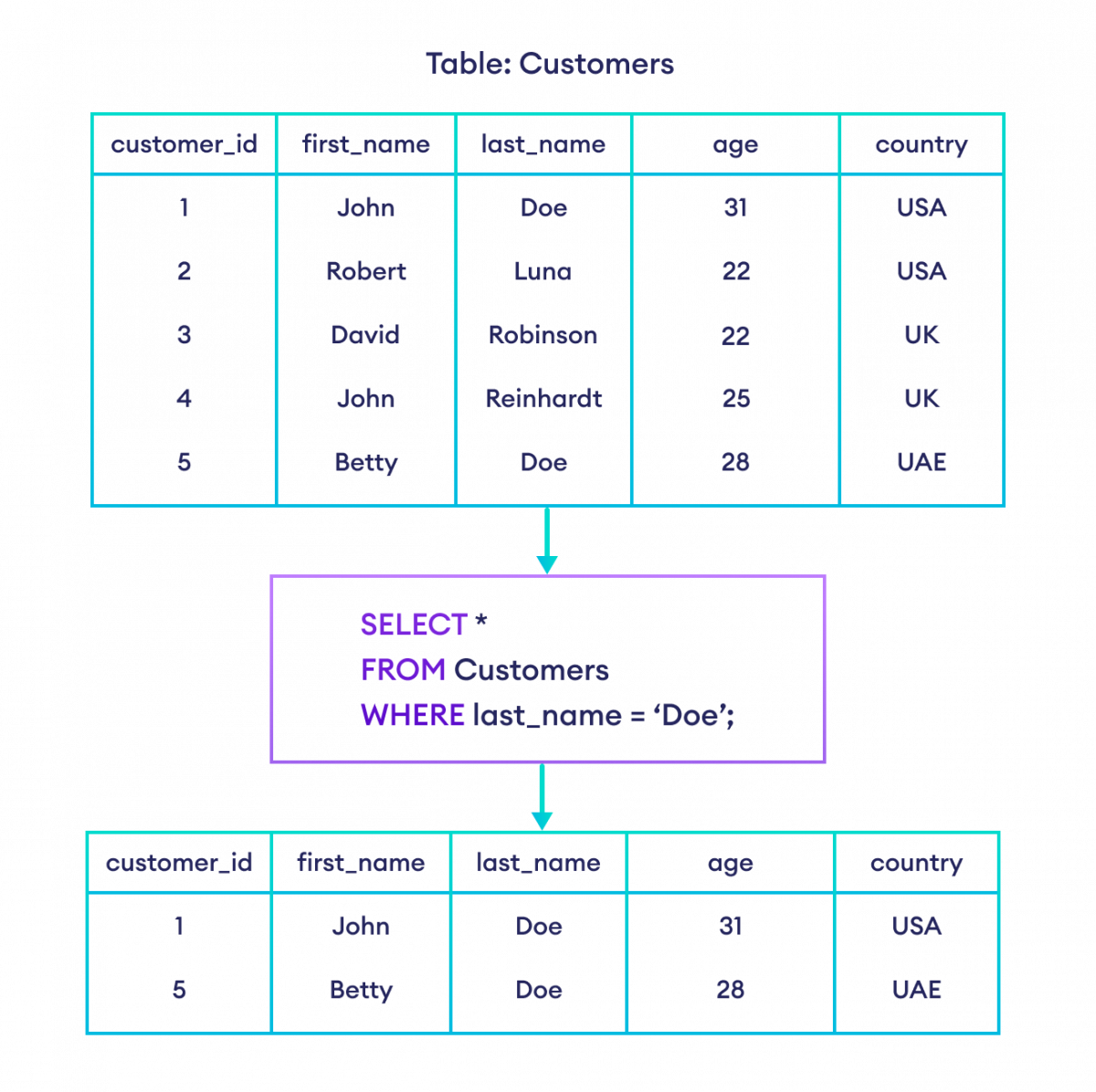
-- select all columns from the customers table with last_name 'Doe'
SELECT *
FROM Customers
WHERE last_name = 'Doe';Here, the SQL command selects all customers from the Customers table with the last_name Doe.
Let's look at another example.
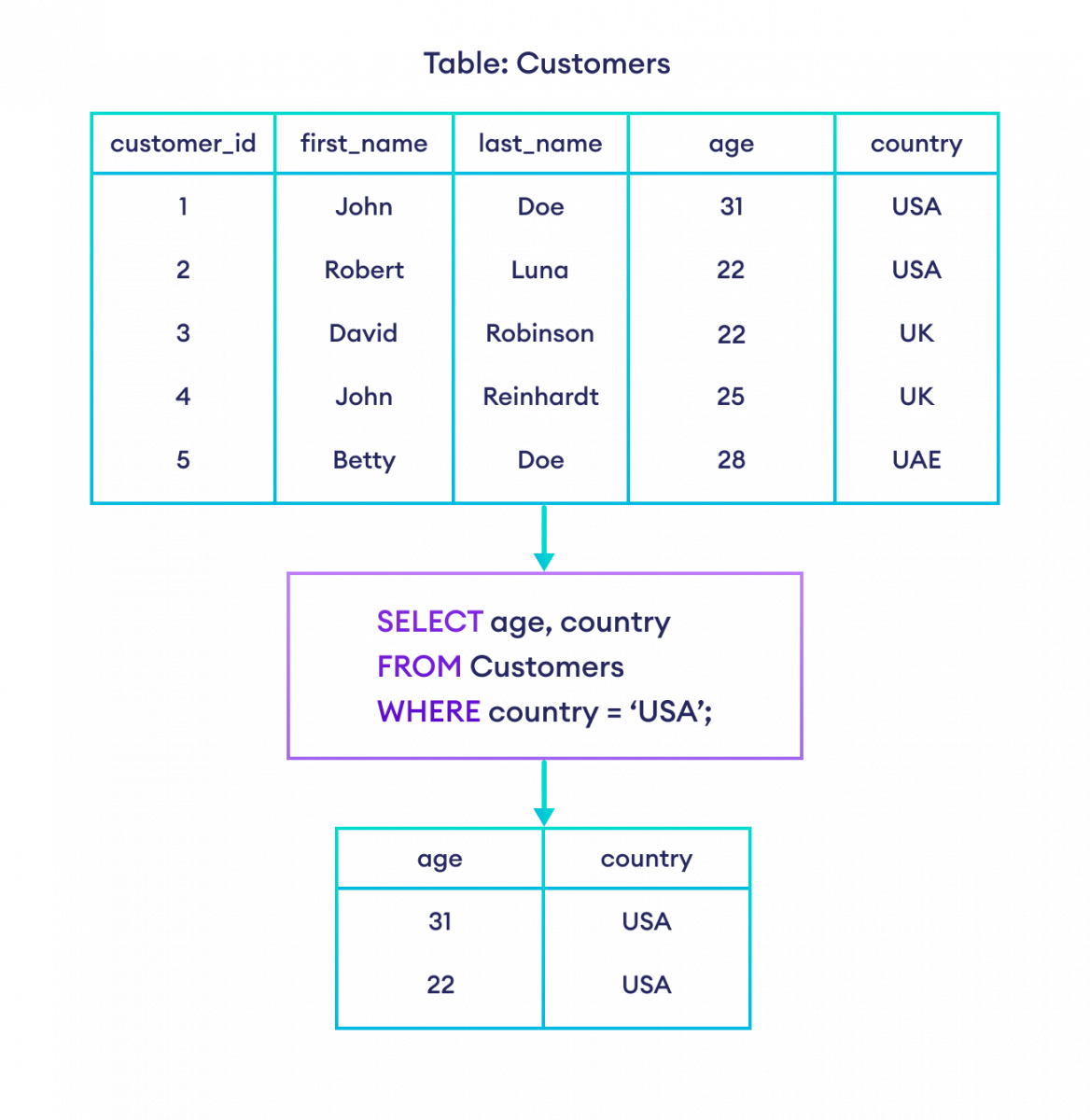
-- select age and country columns from customers table where the country is 'USA'
SELECT age, country
FROM Customers
WHERE country = 'USA';Here, the SQL command selects the age and country columns of all the customers whose country is USA.
We can also use the WHERE clause with the UPDATE statement to edit existing rows in a database table.
Note: In SQL, we must enclose textual data inside either single or double quotations like 'USA'.
SQL Operators
The WHERE clause uses operators to construct conditions. Some of the commonly used operators are:
1. Equal to Operator (=)
-- select all columns from Customers table with first name 'John'
SELECT *
FROM Customers
WHERE first_name = 'John';The above SQL command selects all the customers from the Customers table having first_name John.
2. Greater than (>)
-- select all columns from Customers table with age greater than 25
SELECT *
FROM Customers
WHERE age > 25;The above SQL command selects all the customers from the Customers table whose age is greater than 25.
3. AND Operator (AND)
-- select all columns from Customers table with last_name 'Doe' and country 'USA'
SELECT *
FROM Customers
WHERE last_name = 'Doe' AND country = 'USA';The above SQL command selects all the customers from the Customers table having last_name Doe and country USA.
Note: If none of the rows meet the WHERE clause condition, an empty result set is returned.
To learn more about all the SQL operators in detail, visit SQL Operators.
Also Read: