CSS font-stretch property is used to widen or narrow the text on a webpage. For example,
body {
font-family: Arial, sans-serif;
}
p.normal {
font-stretch: normal;
}
p.condensed {
font-stretch: condensed;
}
Browser Output

Here, font-stretch: condensed narrows the width of characters.
css-font-stretch-syntax CSS Font Stretch Syntax
The font-stretch property has the following syntax,
font-stretch: normal | semi-condensed | condensed | extra-condensed | ultra-condensed | semi-expanded | expanded | extra-expanded | ultra-expanded
The possible value for CSS font-stretch are shown in the following table:
| Font Style Values | Description |
|---|---|
normal |
default value for font-style, the font appears in normal width |
semi-condensed |
font appears slightly narrower than normal |
condensed |
font appears narrower than semi-condensed |
extra-condensed |
font appears narrower than condensed |
ultra-condensed |
font appears narrower than extra-condensed |
semi-expanded |
font appears wider than normal |
expanded |
font appears wider than semi-expanded |
extra-expanded |
font appears wider than expanded |
ultra-expanded |
font appears wider than extra-expanded |
percentage |
value between 50% and 200% (inclusive)Negative values are not allowed. |
Example of font-stretch
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8" />
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0" />
<link rel="stylesheet" href="style.css" />
<title>Using font-stretch</title>
</head>
<body>
<p class="ultra-condensed">Ultra-condensed text</p>
<p class="extra-condensed">Extra-condensed text</p>
<p class="condensed">Condensed text</p>
<p class="semi-condensed">Semi-condensed text</p>
<p class="normal">Normal text</p>
<p class="semi-expanded">Semi-expanded text</p>
<p class="expanded">Expanded text</p>
<p class="extra-expanded">Extra-expanded text</p>
<p class="ultra-expanded">Ultra-expanded text</p>
</body>
</html>
body {
font-family: Arial, Helvetica, sans-serif;
}
/* sets font-stretch to Ultra-condensed*/
p.ultra-condensed {
font-stretch: ultra-condensed;
}
/* sets font-stretch to Extra-condensed*/
p.extra-condensed {
font-stretch: extra-condensed;
}
/* sets font-stretch to Condensed */
p.condensed {
font-stretch: condensed;
}
/* sets font-stretch to Semi-condensed */
p.semi-condensed {
font-stretch: semi-condensed;
}
/* sets font-stretch to Normal */
p.normal {
font-stretch: normal;
}
/* sets font-stretch to Semi-expanded */
p.semi-expanded {
font-stretch: semi-expanded;
}
/* sets font-stretch to Expanded */
p.expanded {
font-stretch: expanded;
}
/*sets font-stretch to Extra-expanded */
p.extra-expanded {
font-stretch: extra-expanded;
}
/* sets font-stretch to Ultra-expanded */
p.ultra-expanded {
font-stretch: ultra-expanded;
}
Browser Output
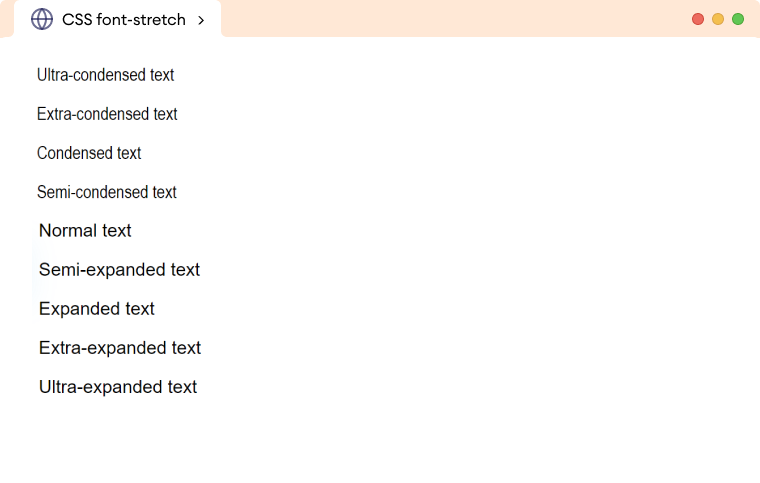
In the above example, the output shows the text with different widths based on the different font-stretch values.
Note: The font-stretch property will have no effect if the current font doesn't support the condensed and expanded faces.